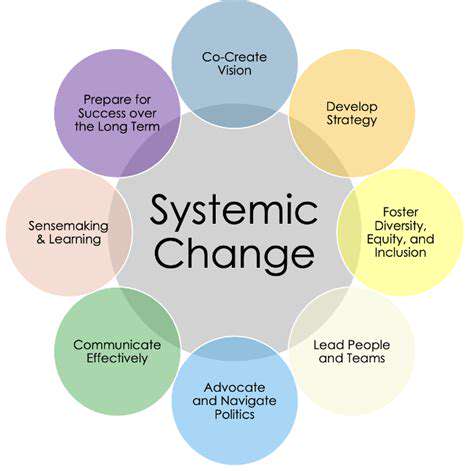
From Linear to Circular: A Systemic Shift in Fashion
Circular fashion models are diverse and innovative, encompassing various approaches to reduce waste and maximize resource utilization. These models include initiatives such as extending the lifespan of garments through repair and reuse programs, designing products for recyclability and decomposability, and implementing closed-loop systems that recover and repurpose materials. These efforts, when successfully implemented, can drastically reduce the environmental footprint of the industry.
One particularly promising strategy is the development of innovative textile recycling technologies. This helps to recover valuable materials from discarded garments, reducing the need for virgin resources and minimizing landfill waste. These processes create a more sustainable and efficient system that benefits both the environment and the economy.
Another important element is the rise of rental and sharing platforms. These platforms allow consumers to access clothing items without owning them, reducing the overall consumption rate and promoting a more mindful approach to fashion. This model also encourages creative reuse and reduces the pressure to continuously purchase new items. Ultimately, these models contribute to a more sustainable future for the fashion industry.
By embracing circularity, the fashion industry can contribute to a more sustainable future while also adapting to evolving consumer preferences and demands. This shift towards sustainability is not just about reducing harm; it's about creating a more responsible and equitable fashion industry for generations to come.
Effective training programs are crucial for success in the hospitality industry. Well-trained staff are better equipped to handle guest needs, provide exceptional service, and maintain a positive image for the establishment. This encompasses everything from basic customer service etiquette to specialized knowledge of products, services, and procedures. Training fosters a consistent and high-quality experience for every guest, which is paramount in today's competitive market.
Embracing Responsible Consumption and Consumption Patterns
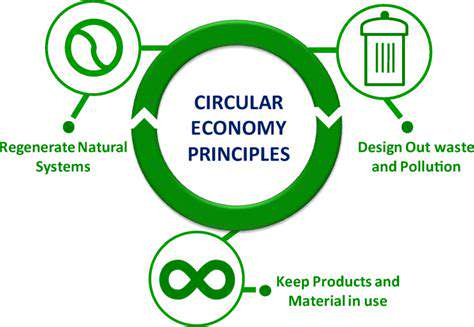
Understanding the Shift from Linear to Circular Consumption
The traditional linear take-make-dispose model of consumption is increasingly unsustainable. It relies on endless extraction of resources, leading to environmental degradation, resource depletion, and significant waste generation. This model is fundamentally incompatible with the finite nature of our planet's resources. Shifting to a circular economy, where resources are kept in use for as long as possible, is crucial for mitigating these challenges and building a more sustainable future.
This transition necessitates a fundamental change in mindset, moving away from a culture of disposability and embracing a more conscious and responsible approach to consumption. The circular model emphasizes reuse, repair, and recycling, minimizing waste and maximizing the lifespan of products.
The Importance of Reducing Waste and Promoting Reuse
A key aspect of responsible consumption is reducing waste at the source. This involves making conscious choices about the products we buy, opting for durable, repairable items over disposable ones. Choosing products with a longer lifespan and considering the environmental impact of their entire lifecycle is essential. We can also promote reuse by actively seeking out products designed for reuse and by repairing existing items rather than immediately replacing them.
By embracing reuse and repair, we can significantly reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills and conserve valuable resources. This approach also supports local economies, as repair services and reuse initiatives can create jobs and foster a sense of community.
The Role of Design in Fostering Circularity
Product design plays a critical role in shaping consumption patterns. Designing products for durability, repairability, and recyclability is essential for transitioning towards a circular economy. This includes incorporating materials that are easily recycled or can be reused in new products, as well as designing products with modular components that can be easily disassembled and repurposed. Innovative design solutions are vital for creating a truly circular system where products are not simply discarded but are continuously reintegrated into the economy.
Encouraging Consumer Awareness and Engagement
Consumer awareness and engagement are crucial for driving the transition to circular consumption. Educating consumers about the environmental impact of their choices and providing them with information about products' lifecycle assessments can empower them to make more sustainable decisions. Transparency in supply chains and clear labeling of products based on their environmental performance are essential steps in fostering informed consumer choices.
Promoting awareness campaigns and providing access to repair services and reuse initiatives can further encourage consumers to adopt more circular consumption patterns. Encouraging a culture of conscious consumption is essential for achieving a more sustainable future.
Policy and Infrastructure Support for Circularity
Government policies and infrastructure development are vital for creating a supportive environment for circular consumption. Policies that incentivize the production and consumption of sustainable products, such as tax breaks for eco-friendly businesses and extended producer responsibility schemes, can accelerate the transition. Investing in infrastructure for waste collection, recycling, and repair services is also critical for supporting the circular economy.
Collaboration between businesses, governments, and consumers is essential to creating a comprehensive and effective framework for fostering a circular economy. The creation of robust policies and infrastructure will drive innovation and ensure the successful transition from linear to circular consumption patterns.