The Future of Fashion Production: Designing for Circularity: New Visions
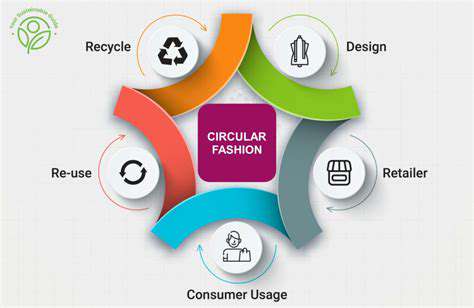
Circular fashion offers a transformative alternative to the current linear model. By embracing principles of reuse, repair, and recycling, circularity aims to minimize waste, conserve resources, and create a more sustainable fashion system. This approach necessitates a complete reimagining of the design, production, and consumption processes within the fashion industry, emphasizing durability, longevity, and the use of recycled or renewable materials. Circular fashion encourages conscious consumer choices, promoting the repair and reuse of garments, extending their lifespan, and reducing the demand for new textiles.
Key components of a circular fashion model include the development of innovative materials, such as recycled fabrics and bio-based fibers. Furthermore, fostering a culture of repair and extending the lifespan of garments through innovative design and maintenance techniques is crucial. This approach not only reduces waste but also creates opportunities for job creation within the repair and recycling sectors, bolstering local economies and fostering a more resilient fashion industry. Ultimately, embracing circularity in fashion is not just an environmental imperative but also a pathway toward a more equitable and sustainable future.
Circular fashion also encourages businesses to adopt more sustainable practices. This involves transparency in supply chains, ethical labor practices, and commitment to minimizing environmental impacts throughout the entire product lifecycle. These shifts are not merely about environmental protection; they are about creating a more responsible and equitable industry, one that considers the long-term well-being of both people and the planet.
Promoting rental, sharing, and resale platforms for clothing can also contribute to a more circular fashion system. These initiatives encourage a shift away from the 'fast fashion' mentality and towards a more mindful and responsible approach to clothing consumption.
The transition to a circular fashion model requires a collective effort, involving designers, manufacturers, retailers, and consumers. By working together, we can create a system where fashion is not only stylish but also environmentally responsible and socially equitable.
Rethinking Design for Durability and Repurposing

Designing for Longevity: A Shift in Perspective
Traditional design often prioritizes aesthetics and functionality over the long-term lifespan of a product. This approach frequently leads to products that are stylish but lack the durability needed to withstand repeated use and environmental factors. Shifting the focus to durability from the outset can significantly enhance a product's value proposition, extending its useful life and minimizing the environmental impact of its eventual disposal.
Material Selection and Testing: Critical Components
Careful material selection is paramount in ensuring product longevity. Choosing materials with inherent resilience and resistance to wear, tear, and environmental degradation is crucial. Rigorous testing protocols, including stress tests, impact tests, and accelerated aging simulations, are essential to identify potential weaknesses and ensure the product can withstand anticipated usage scenarios.
Manufacturing Processes: Precision and Quality
Manufacturing processes play a vital role in determining the durability of a product. Implementing precision manufacturing techniques, using high-quality components, and ensuring consistent quality control throughout the production process are critical to creating a durable end product. Efficient manufacturing practices also contribute to cost-effectiveness, while maintaining a commitment to quality.
User Experience and Ergonomics: Enhancing Durability through Practicality
Designing for user experience and ergonomics goes beyond aesthetics. Intuitive design, comfortable handling, and easy maintenance contribute to a product's perceived durability. A well-designed product is easier to use, reduces the risk of accidental damage, and makes maintenance more accessible, which all contribute to a longer lifespan.
Environmental Considerations: Eco-Friendly Durability
Incorporating environmental considerations into the design process is a critical aspect of achieving true durability. Using sustainable materials, minimizing waste during manufacturing, and designing for recyclability can create products that are both durable and environmentally responsible. This approach fosters a sustainable future and builds brand reputation.
Lifecycle Assessment: A Holistic Approach
Conducting a thorough lifecycle assessment (LCA) can provide valuable insights into the environmental impact of a product throughout its entire lifespan. From material sourcing to manufacturing, use, and disposal, an LCA helps identify potential environmental issues and inform design decisions aimed at minimizing environmental impact. This holistic approach emphasizes the interconnectedness of design, manufacturing, and environmental responsibility.
Maintenance and Repair: Extending the Lifespan
Designing for maintainability and ease of repair is crucial for extending a product's lifespan. Clear instructions, readily available parts, and simple repair procedures empower users to maintain their products effectively. By enabling repairs, a product's lifespan is significantly extended and its environmental impact is reduced.
Circular Manufacturing Processes: A Holistic Approach
Circular Manufacturing Processes: A Fundamental Shift
Circular manufacturing processes represent a fundamental paradigm shift in the fashion industry, moving away from the traditional linear take-make-dispose model. This shift necessitates a holistic approach, encompassing the entire lifecycle of fashion products, from raw material sourcing to end-of-life management. This transformation is critical to mitigating environmental harm, promoting resource efficiency, and building a more sustainable future for fashion.
Material Selection and Sourcing: Prioritizing Recycled and Renewable Resources
A crucial aspect of circular manufacturing involves prioritizing the use of recycled and renewable materials in the production of fashion products. This includes utilizing recycled fibers like recycled polyester and cotton, as well as exploring innovative bio-based materials derived from agricultural waste or other renewable sources. By selecting these materials, manufacturers can reduce their reliance on virgin resources and lessen the environmental footprint of their products.
Design for Disassembly and Remanufacturing: Extending Product Lifespan
Designing fashion products for disassembly and remanufacturing is another key element of circular manufacturing. This involves incorporating modular designs and using standardized components, enabling easier disassembly and component reuse. Such strategies will significantly extend the lifespan of products, thereby reducing the need for new material extraction and minimizing waste.
Closed-Loop Systems and Waste Reduction Strategies: A Sustainable Approach
Implementing closed-loop systems is essential for minimizing waste generation throughout the entire lifecycle of a fashion product. This approach involves collecting and reprocessing used garments and materials, turning them into new products or components. This approach not only reduces waste but also fosters a circular economy where resources are continually reused and recycled.
Transparency and Traceability: Building Trust and Accountability
Transparency and traceability are vital for establishing trust and promoting accountability in circular manufacturing processes. Clear and consistent labeling of materials, production processes, and recycling instructions enables consumers to make informed decisions. This transparency also allows for greater scrutiny and accountability throughout the supply chain.
Collaboration and Partnerships: Fostering Innovation
Circular manufacturing requires collaboration and partnerships between various stakeholders, including designers, manufacturers, retailers, and consumers. Collaboration can lead to innovative solutions and the development of shared best practices. By working together, the fashion industry can accelerate the transition to a more sustainable and circular model.
Consumer Engagement and Education: Driving Change
To achieve true circularity in the fashion industry, consumer engagement and education are crucial. Educating consumers about the benefits of circular fashion and empowering them to make conscious choices, such as choosing durable and repairable garments, will drive demand for sustainable products and incentivize businesses to adopt circular practices. Ultimately, consumer engagement is critical to the long-term success of circular manufacturing.
Personalized marketing in real estate leverages AI to understand individual buyer preferences and tailor the entire property search journey. This goes beyond simple demographics; AI analyzes browsing history, saved properties, and even social media activity to create highly targeted experiences. For example, a buyer interested in modern, open-concept apartments in a specific neighborhood might receive tailored recommendations, curated property listings, and even virtual tours of properties that perfectly align with their preferences. This personalized approach fosters a stronger connection with potential buyers, leading to increased engagement and ultimately a higher conversion rate.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Circular Fashion
The Automation of Tasks
Technological advancements have led to significant automation of tasks across various industries. From manufacturing assembly lines to customer service chatbots, machines are increasingly capable of performing complex operations previously reliant on human labor. This automation not only boosts efficiency and productivity but also frees human workers to focus on more strategic and creative endeavors. The ability to automate repetitive tasks allows businesses to allocate resources more effectively and potentially increase profitability.
Furthermore, the automation of tasks often results in reduced errors, as machines can perform actions with greater precision and consistency compared to humans. This leads to higher quality output and improved overall operational efficiency. The integration of automated systems also offers the potential for 24/7 operation, enabling continuous production and service delivery, which can be a major advantage in competitive markets.
The Enhancement of Communication and Collaboration
Technology has revolutionized the way we communicate and collaborate, connecting people across geographical boundaries and facilitating seamless information sharing. Instant messaging platforms, video conferencing tools, and project management software have transformed the workplace, allowing teams to communicate effectively and stay synchronized on projects, regardless of location. This global connectivity fosters innovation by enabling diverse perspectives and ideas to converge.
The ability to share information in real-time through various technological platforms has dramatically improved the speed and efficiency of decision-making processes. This enhanced communication and collaboration allows businesses to respond to market changes more quickly, adapt to new trends, and ultimately increase their ability to compete effectively.
The Transformation of Business Processes
Technology has fundamentally altered the way businesses operate, streamlining processes and enhancing efficiency across the board. From online ordering systems and inventory management software to cloud-based storage and data analysis tools, technological innovations have revolutionized how businesses manage their operations. This transformation enables businesses to optimize their resource allocation and minimize operational costs.
The adoption of technology often leads to improved customer experience. Businesses can provide tailored services, personalize interactions, and offer convenient online platforms for customers to access products and services. These advancements ultimately drive customer satisfaction and loyalty, which are key factors for long-term business success.
The Impact on Consumer Behavior
The pervasive influence of technology has profoundly shaped consumer behavior. From online shopping and social media interactions to mobile banking and streaming services, consumers are increasingly relying on technology for everyday activities. This reliance has created new expectations and demands for products and services. Consumers expect seamless transactions, personalized experiences, and readily available information.
Technological advancements have also fostered greater consumer awareness and empowered them to make more informed decisions. Access to information about products and services, comparative reviews, and online forums empowers consumers to evaluate options and make choices that align with their needs and preferences. This shift in consumer behavior has led to the evolution of business strategies, requiring companies to adapt and innovate to meet the changing demands of a technologically advanced marketplace.
Consumer Engagement and Shifting Consumption Patterns

Consumer Engagement Strategies in the Digital Age
Consumer engagement has become a critical aspect of success for businesses in today's digital landscape. Companies are actively seeking innovative ways to connect with their target audience and foster loyalty. This involves more than simply pushing products or services; it necessitates a deep understanding of consumer needs, preferences, and motivations. Effective engagement strategies often involve creating interactive experiences that resonate with consumers on a personal level. This approach allows brands to build lasting relationships and drive repeat business.
The digital age has fundamentally altered how consumers interact with brands. Social media platforms, online communities, and personalized websites have created new avenues for engagement. Businesses must adapt their strategies to meet consumers where they are, adopting a proactive and responsive approach. This includes actively participating in online conversations, responding to customer feedback, and leveraging data analytics to tailor experiences to individual preferences.
Shifting Consumer Behaviors and Expectations
Consumer behaviors are constantly evolving, driven by factors such as technological advancements, economic shifts, and social trends. Understanding these shifts is crucial for businesses to remain competitive. Companies must anticipate and adapt to changing expectations, ensuring their products and services align with the evolving needs of their target audience. This proactive approach is essential for maintaining relevance and fostering lasting relationships with customers.
Consumers today are more informed and empowered than ever before. They expect transparency, authenticity, and personalized experiences from the brands they engage with. This requires businesses to be responsive to customer feedback, build trust through ethical practices, and consistently deliver on their promises. Consumers are increasingly demanding brands that demonstrate a commitment to social responsibility, environmental sustainability, and ethical sourcing, further shaping their expectations.
Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce and mobile technology has significantly impacted consumer expectations. Consumers now expect seamless and convenient online experiences, including quick order processing, secure payment options, and readily available customer support. Failure to meet these expectations can lead to a loss of customers and damage to brand reputation.
The expectation for instant gratification is also impacting consumer behaviors. Consumers want to receive information and products quickly and efficiently. Businesses need to optimize their processes to meet these expectations, providing quick responses, clear communication, and timely delivery of goods or services.
Consumers are increasingly seeking brands that align with their values. This includes supporting businesses that prioritize social responsibility, environmental sustainability, and ethical sourcing. Understanding and responding to these values-driven consumer behaviors is vital for long-term success.