The Financial Landscape of Circular Fashion Investment
Analyzing Key Metrics for Evaluating Circular Fashion Investments
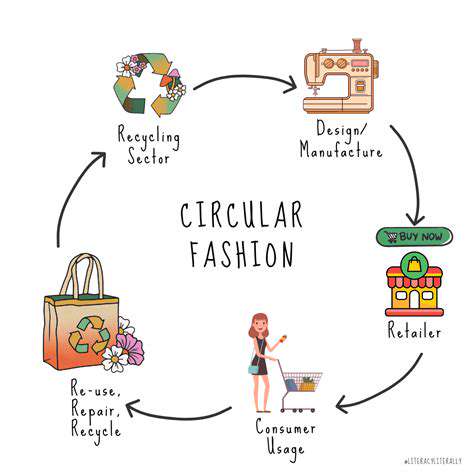
Understanding the Importance of Circularity in Fashion
Circular fashion represents a transformative departure from the outdated linear take-make-dispose approach, emphasizing resource efficiency, waste minimization, and material reuse. This methodology addresses pressing environmental challenges while fostering a more ethical and resilient economic framework. Grasping the intrinsic value of circularity proves indispensable for assessing investments in this evolving sector.
Through implementing closed-loop systems and mitigating environmental harm, circular fashion investments pave the way toward sustainability. The focus extends beyond mere waste reduction to incorporate durable design, repair facilitation, and comprehensive product lifecycle management from creation to disposal.
Assessing Material Circularity and Waste Reduction
Evaluating circular fashion investments requires scrutinizing textile waste reduction and the adoption of recycled or renewable materials. Measuring decreased production waste and the integration of repurposed materials into new designs offers critical insights. Investors should examine specific tactics for waste minimization, including disassembly-friendly designs and cutting-edge recycling methods.
Supply chain transparency remains crucial. Investors require precise metrics regarding recycled material percentages, landfill diversion rates, and impacts on resource consumption. Such data substantiates the investment's tangible contributions to sustainability.
Analyzing Product Longevity and Durability
Circular fashion investments demand evaluation of product durability and repairability. Garments designed for extended use with repair-friendly features demonstrate commitment to prolonging product lifecycles, thereby reducing replacement frequency and environmental strain.
Examining durability-enhancing design elements helps identify promising ventures. Features like reinforced stitching, premium fabrics, and accessible repair guidelines not only boost sustainability but also enhance consumer satisfaction, creating a virtuous cycle.
Evaluating the Economic Viability of Circular Models
While environmental considerations dominate, economic feasibility determines long-term success. Assessing waste reduction cost savings, revenue potential from extended product lifecycles, and sustainable product market demand proves essential.
Investors must analyze profitability prospects through sustainable premium pricing and operational efficiencies gained from waste minimization and resource optimization strategies.
Assessing Supply Chain Transparency and Ethical Practices
Circular fashion investments require rigorous examination of ethical labor practices and supply chain transparency. Investors should verify material sourcing methods, worker conditions, and manufacturing environmental impacts throughout the production cycle.
Comprehensive supply chain audits encompassing fair wages, workplace safety, and regulatory compliance provide critical sustainability indicators.
Measuring Consumer Adoption and Market Demand
Understanding consumer receptiveness to circular fashion products remains paramount. Analyzing market trends, buyer preferences, and premium pricing acceptance for sustainable goods informs investment potential.
Evaluating consumer response to durable designs, repairable products, and extended lifecycles helps gauge commercial viability. Effective marketing and consumer education strategies significantly influence success.
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape and Future Trends
The evolving regulatory environment for circular fashion significantly impacts business model feasibility. Monitoring government policies, including environmental standards and financial incentives, ensures long-term sustainability.
Anticipating technological advancements, shifting consumer behaviors, and regulatory changes enables future-proof investments in this dynamic sector.
The Future of Circular Fashion Investments: Navigating Challenges and Opportunities

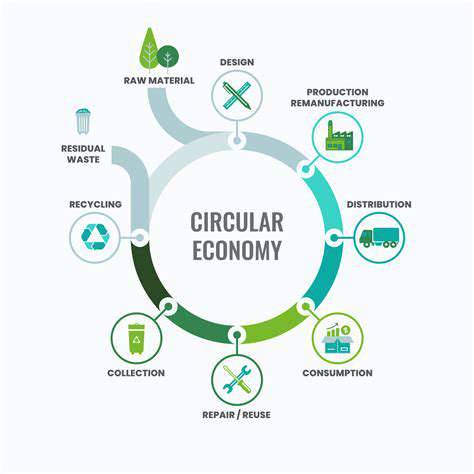
Circular Fashion: A Paradigm Shift
Fashion's future is inextricably linked with circularity principles. This fundamental transformation redefines clothing design, production, consumption, and disposal processes. Rather than perpetuating the unsustainable linear model, circular fashion establishes closed-loop systems that conserve resources and minimize waste, promising an ethical, sustainable industry.
This transition demands comprehensive system overhaul encompassing design methodologies, manufacturing processes, and consumer behaviors. By embracing durability, repairability, and recyclability principles, we can achieve equitable, sustainable fashion ecosystems.
Design for Durability and Longevity
Circular fashion prioritizes durable garment design through premium materials, robust construction, and timeless aesthetics. Extended product use reduces demand for new items and environmental impact.
Repairability and Upcycling: Extending Garment Lifespan
Beyond durability, designs should facilitate repairs through accessible services or kits. Upcycling transforms existing garments into new creations, dramatically reducing textile waste. This approach benefits ecosystems while fostering consumer creativity and resourcefulness.
Sustainable Materials and Manufacturing Processes
Circular fashion necessitates sustainable, recycled materials and eco-conscious manufacturing. Implementing processes that reduce resource consumption, minimize chemical use, and ensure ethical labor practices creates fashion systems respecting both environment and workers.
Consumer Engagement and Responsibility
Circular fashion success ultimately depends on consumer participation. Educating buyers about sustainable choices, promoting repair initiatives, and encouraging conscious consumption habits drive meaningful change. Equipping consumers with knowledge and tools enables collective progress toward responsible, eco-friendly fashion futures.