The Environmental Impact of Chemical Discharges from Fashion Production
The Hidden Dangers of Textile Dyeing
The global textile industry depends on dyeing processes that would make a chemist cringe. To achieve those perfect colors, manufacturers brew toxic soups of synthetic dyes, fixatives, and chemical auxiliaries. Many commercial dyes contain carcinogenic aromatic amines that persist stubbornly in the environment. When these chemicals enter waterways, they don't simply dilute - they accumulate in sediment and living organisms, creating long-term hazards.
Wastewater Contamination and its Impact
Textile dyehouses generate wastewater so contaminated it can stain rivers for miles downstream. In developing nations where most dyeing occurs, up to 90% of this toxic effluent flows untreated into local waterways. The results are apocalyptic - rivers running blood red with azo dyes, fish populations collapsing, and drinking water sources becoming dangerously polluted. Some communities near textile hubs can identify the season's fashion colors just by observing their local river.
Modern wastewater treatment could mitigate this disaster, but the costs deter implementation. Reverse osmosis and advanced oxidation systems require investments that undercut fast fashion's razor-thin margins. Without regulatory pressure or consumer backlash, factories will continue prioritizing profits over pollution controls.
Sustainable Alternatives and Responsible Practices
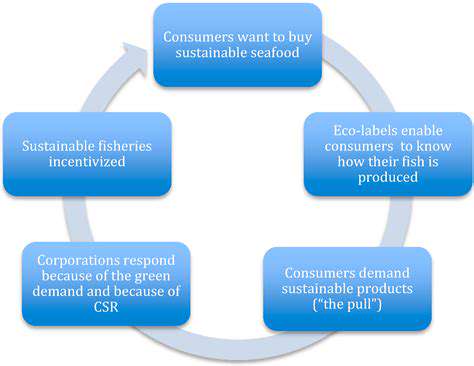
Hope emerges from ancient traditions and cutting-edge innovation. Natural dyes from plants like indigo and madder root offer vibrant colors without synthetic toxins. New enzymatic and supercritical CO2 dyeing technologies could slash water use by 90% while eliminating hazardous wastewater. Some forward-thinking brands now implement closed-loop systems where every chemical gets recycled.
The path forward requires radical transparency. Consumers must demand full supply chain disclosure while supporting brands investing in clean technology. Regulators need to enforce strict pollution standards and ban the most hazardous chemicals. With concerted effort, we can transform fashion from a pollution source into a sustainability leader.
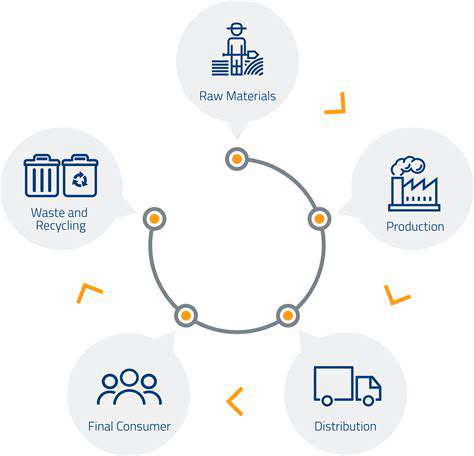
Manufacturing Processes: A Cascade of Waste
Material Selection and Preparation
The foundation of sustainable manufacturing begins with intelligent material choices. Conventional textiles often prioritize cost over environmental impact, but alternatives exist. Organic cotton uses 91% less water than conventional crops. Recycled polyester diverts plastic waste from landfills. Tencel lyocell comes from sustainably harvested eucalyptus processed in closed-loop systems. Each choice ripples through the entire production chain.
Casting and Molding Techniques
Traditional manufacturing wastes staggering amounts of material through trimming and defective parts. New digital fabrication methods like 3D knitting create garments with virtually zero material waste. Some innovators now grow materials from mycelium or bacterial cellulose, forming products without traditional manufacturing's energy-intensive processes. The future belongs to these biological manufacturing platforms.
Machining and Fabrication Processes
Precision cutting technologies like laser and waterjet systems minimize fabric waste dramatically. Digital pattern optimization can increase material utilization from the industry standard of 80% to over 95%. Some factories now recycle fabric scraps into new yarns or insulation materials, creating closed-loop systems that mimic nature's efficiency.
Assembly and Finishing Operations
The final assembly often hides surprising waste. Modular design allows garments to be disassembled for recycling rather than landfilling. Chemical-free finishing techniques like laser etching replace toxic treatments. Some brands now use RFID tags to track garments through their entire lifecycle, enabling responsible end-of-life recycling.
Quality Control and Inspection
Artificial intelligence now spots manufacturing defects earlier than human inspectors, reducing waste from flawed products. Blockchain technology creates immutable records of sustainable practices. These digital innovations help hold brands accountable while minimizing production waste at every stage.