The Future of Ownership: Exploring Fashion Rental Services
Consumer behavior has fundamentally changed. Rather than accumulating items, people now seek temporary access to diverse wardrobes without long-term commitment. Younger generations particularly embrace this trend, valuing flexibility and variety over permanent ownership of clothing.
Sustainability and Reduced Waste
Subscription fashion models gain traction partly due to growing environmental awareness. Fast fashion's ecological impacts - from textile waste to pollution - have become increasingly apparent. By facilitating repeated use of garments, subscription services help decrease demand for new production and promote thoughtful consumption patterns.
Many subscription companies collaborate with eco-conscious brands, appealing to consumers who prioritize sustainability. This alignment reflects broader societal shifts toward environmentally responsible purchasing decisions.
Curated Experiences and Personalization
Fashion subscriptions frequently offer more than just clothing. Providers often tailor selections to individual preferences, offering styling advice and personalized recommendations. This customized approach enhances customer engagement while making fashion more accessible across diverse body types and style preferences.
The experience often extends beyond physical items, with some services including style consultations, exclusive events, and community features that foster deeper brand connections.
Economic Benefits and Accessibility
Subscription models create financial advantages for both consumers and businesses. Customers enjoy cost-effective wardrobe access, including opportunities to wear high-end pieces without full purchase commitments. Businesses benefit from predictable revenue streams and enhanced customer loyalty through ongoing engagement.
The model's flexibility allows companies to adapt quickly to shifting consumer preferences while offering dynamic fashion experiences that traditional retail struggles to match.
The Future of Ownership in Fashion
Subscription services represent more than a passing trend - they signal a fundamental industry shift toward access-based consumption. While traditional ownership won't disappear entirely, the fashion landscape increasingly emphasizes temporary access, sustainability, and personalized experiences.
As technology advances, we can expect more innovative subscription offerings that further transform how consumers interact with fashion, potentially reshaping the entire industry toward more sustainable practices.
Beyond Convenience: Environmental and Economic Benefits

Beyond the Disposable: Understanding Single-Use Plastics
Single-use plastics create lasting environmental damage despite their convenience. These materials may persist for centuries in ecosystems, accumulating in landfills and oceans while harming marine life. Their petroleum-based production also contributes significantly to climate change, necessitating urgent alternatives.
The Plastic Pollution Crisis: A Global Problem
Plastic contamination affects every continent, disrupting ecosystems worldwide. From microscopic plastic particles entering food chains to massive oceanic garbage patches, the consequences demand immediate attention. This widespread pollution threatens biodiversity and could permanently alter delicate ecological balances.
The Impact on Marine Life: A Silent Tragedy
Sea creatures frequently consume plastic debris, often with fatal results. The long-term effects on marine populations remain under study, but current evidence suggests severe impacts. Entanglement in plastic waste presents another critical threat to ocean ecosystems already under stress.
Sustainable Alternatives: A Path Forward
Reusable products - from shopping bags to food containers - offer practical solutions to reduce plastic dependence. Adopting these alternatives represents both environmental responsibility and personal commitment to sustainability. Making conscious choices today can preserve planetary health for future generations.
The Role of Education and Awareness: Empowering Individuals
Public understanding of plastic's environmental impact remains crucial for driving change. Effective education campaigns can motivate sustainable behavior shifts while demonstrating the benefits of reusable alternatives. Knowledge empowers consumers to make environmentally responsible decisions.
Policy Changes and Industry Responsibility: Systemic Solutions
Governments and corporations must collaborate to address plastic pollution through policy reforms and sustainable innovation. Businesses play a critical role in developing biodegradable alternatives while policies should incentivize environmentally friendly materials over single-use plastics.
The Economic Implications: A Shift Towards Sustainability
While transitioning from plastics requires initial investment, the long-term economic benefits outweigh costs. Reduced healthcare expenses, environmental preservation, and new green industry opportunities all contribute to a more sustainable economy. Embracing sustainability drives both ecological and economic resilience.
The Evolution of the Fashion Retail Landscape

The Rise of Department Stores
Department stores revolutionized shopping in the late 19th century by consolidating diverse merchandise under single roofs. These retail giants transformed consumer habits by offering comprehensive fashion selections alongside household goods. Their emergence fundamentally changed fashion accessibility and established new retail standards that persist today.
The department store model succeeded by combining product variety with convenience, creating exciting shopping experiences that drove fashion trends. This approach democratized style access while fostering continuous industry innovation.
The Impact of Mass Production
Industrial manufacturing techniques dramatically reduced clothing costs, making fashion accessible to broader populations. This affordability revolution transformed retail strategies and consumer expectations, enabling mass-market fashion distribution.
Standardized sizing and production facilitated trend-focused marketing while influencing design directions. The efficiency of mass production allowed retailers to respond quickly to shifting consumer preferences at scale.
The Digital Revolution in Retail
E-commerce has radically reshaped fashion retail, offering unprecedented convenience and global reach. Online platforms enable brands of all sizes to connect with worldwide audiences while providing personalized shopping experiences. Digital channels have become essential for modern fashion commerce, facilitating real-time customer engagement and detailed product exploration.
Technology continues to redefine fashion retail through advanced analytics, virtual fitting tools, and seamless omnichannel experiences that blend physical and digital shopping.
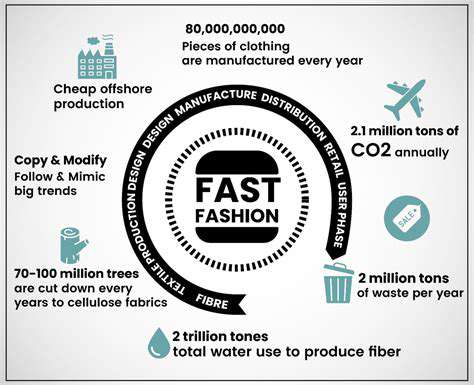
The Rise of Fast Fashion
Fast fashion emerged as a dominant retail force by delivering affordable, trend-responsive clothing. This model's rapid production cycles satisfy consumer demand for constant novelty while maintaining low price points. However, the environmental and ethical costs of fast fashion have sparked growing criticism and calls for more sustainable alternatives.
While successful commercially, fast fashion's emphasis on disposability and rapid turnover raises significant concerns about resource consumption and labor practices in global supply chains.
Challenges and the Road Ahead

Navigating the Economic Landscape
Businesses face complex economic conditions marked by market volatility and inflationary pressures. Adapting to these challenges requires strategic financial planning and operational agility. Proactive risk management becomes essential for maintaining stability during uncertain times.
Diversification and efficiency improvements can help organizations weather economic fluctuations while positioning themselves for future growth opportunities.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
Rapid technological progress continues disrupting industries across sectors. Artificial intelligence, automation, and advanced analytics present both opportunities and challenges for workforce development and business models.
Companies must invest in continuous learning and technology adoption to remain competitive in increasingly digital marketplaces.
Maintaining a Strong Workforce
Attracting and retaining skilled employees remains critical for organizational success. Competitive compensation, professional development opportunities, and positive workplace cultures help build committed, productive teams. Employee engagement directly correlates with business performance and long-term sustainability.
Addressing Environmental Concerns
Sustainability has become a business imperative rather than optional consideration. Regulatory requirements, consumer expectations, and investor priorities all drive companies toward greener practices that reduce environmental impacts.
While implementing sustainability measures requires investment, the long-term benefits - including cost savings and brand enhancement - often justify the expenditure.
Global Interconnectedness and Collaboration
Modern businesses operate in increasingly interconnected global markets. Success requires cultural awareness, ethical business practices, and effective cross-border partnerships. International collaboration unlocks new opportunities while demanding sensitivity to regional differences and global challenges.