The Human Cost of Fast Fashion: Understanding Ethical Sourcing

Hidden Hazards in the Gig Economy
The gig economy, while offering flexibility, often masks precarious working conditions. Workers in this sector frequently face instability, with unpredictable income streams and limited access to benefits like health insurance or paid time off. This lack of security can lead to significant financial stress and impact overall well-being. Many gig workers are forced to juggle multiple gigs to maintain a stable income, further complicating their lives and often leading to burnout.
Furthermore, the lack of regulation in some gig sectors can expose workers to unsafe working environments. The absence of clear guidelines and enforcement mechanisms creates a breeding ground for exploitative practices. This vulnerability is further exacerbated by the often-blurred lines between employee and contractor status, making it difficult for workers to assert their rights or secure recourse for issues like unsafe working conditions.
Exploitation in the Shadow of Automation
Technological advancements, while boosting productivity in many sectors, can paradoxically create new avenues for the exploitation of workers. As automation takes over repetitive tasks, there's a growing need for human workers to fill roles that are still essential for the completion of a product or service. However, these workers are often relegated to lower-paying positions with fewer benefits and less job security. A common theme is a lack of transparency in compensation structures, making it challenging for workers to understand their rightful compensation.
The potential for algorithmic bias in hiring and compensation practices is a concern that must be addressed. These biases can perpetuate inequalities and limit opportunities for certain groups of workers. The need for ethical considerations and transparency in algorithmic decision-making is crucial to ensure fair and equitable employment practices.
The Impact of Underpaid Workers on Businesses
While businesses may initially benefit from low-cost labor, the long-term consequences of underpaying workers can be detrimental to the business's overall success. Employees who are undervalued and underpaid tend to be less productive and motivated, leading to lower quality work and higher turnover rates. This can result in higher recruitment and training costs in the long run. This cycle of exploitation ultimately harms both the workers and the businesses they serve.
It's important to acknowledge that a fair and equitable workforce is a crucial component of a healthy and thriving business environment. Maintaining a positive working environment leads to increased job satisfaction and productivity, ultimately benefiting the business in the long term.
Lack of Access to Essential Resources
Many workers, particularly in marginalized communities, face significant barriers to accessing essential resources, including healthcare, childcare, and transportation. These barriers are often exacerbated by precarious employment conditions, leading to a vicious cycle of vulnerability and disadvantage. The lack of access to these resources can significantly hinder a worker's ability to perform their job effectively and contribute to their overall well-being.
The Importance of Transparency and Regulation
Enhanced transparency in employment practices and robust regulations are vital for protecting workers' rights and ensuring fair labor standards. Transparency in compensation structures, benefits, and working conditions is essential for workers to make informed decisions about their employment. Clear regulations can establish clear boundaries and prevent exploitative practices. This will help to ensure that workers are treated fairly and have the necessary protections in place.
Effective enforcement mechanisms are critical to ensure that these regulations are not just on paper but are actively implemented and enforced. Monitoring and reporting mechanisms can help to identify and address instances of abuse and ensure accountability.
The Need for Collective Action and Advocacy
Collective action and advocacy play a crucial role in empowering workers and raising awareness about hidden labor issues. By coming together, workers can collectively negotiate for better wages, benefits, and working conditions. Organizations and activists focused on worker rights can amplify the voices of those who are often unheard. The sharing of experiences and the solidarity between workers is crucial in achieving positive change.
Environmental Impact: A Planet Burdened by Fast Fashion's Waste
The Textile Treadmill: A Cycle of Consumption
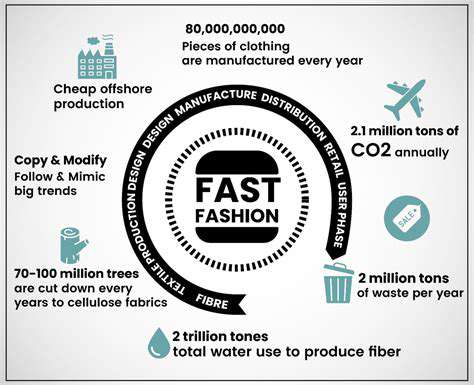
Fast fashion's relentless cycle of new trends and ever-cheaper garments fuels a constant demand for production, leading to a staggering amount of textile waste. This relentless pursuit of the latest styles, often at the expense of ethical and sustainable practices, creates a massive environmental footprint. The pressure to keep up with the constantly evolving fashion industry drives consumers to replace garments more frequently, contributing to the growing mountain of discarded clothing that ends up in landfills or incinerators.
Water Pollution: A Silent Crisis in the Fashion Industry
The production of textiles, particularly synthetic fibers like polyester, requires immense amounts of water. This water often becomes contaminated with harmful chemicals used in dyeing and finishing processes. These pollutants, including heavy metals and dyes, seep into local water sources, threatening aquatic ecosystems and potentially contaminating drinking water supplies. The environmental impact of this water pollution is profound and far-reaching, affecting not only the immediate surroundings but also the broader ecosystem.
Landfill Overflow: A Global Environmental Concern
The sheer volume of discarded clothing filling landfills worldwide presents a significant environmental problem. Landfills take up valuable land, releasing harmful greenhouse gases as organic matter decomposes. Furthermore, the disposal of textiles contributes to the growing problem of plastic pollution as many fast fashion items contain synthetic fibers that are not easily biodegradable. This creates a vicious cycle of environmental degradation, impacting both immediate surroundings and global ecosystems.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Growing Threat to Our Planet
The production and transportation of fast fashion garments contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. From the energy used in manufacturing to the fuel consumed in shipping goods across continents, the carbon footprint of fast fashion is substantial. These emissions contribute to climate change, exacerbating extreme weather events and threatening biodiversity. The environmental cost of this production and distribution process is far greater than the price tag on the garments themselves.
Chemical Contamination: A Hidden Threat to Health and the Environment
The use of harmful chemicals in the dyeing and finishing processes of fast fashion garments poses a significant threat to both human health and the environment. These chemicals, often released into the air and water, can have detrimental effects on human health, impacting respiratory systems and potentially causing long-term health issues. Exposure to these chemicals also jeopardizes the health of ecosystems, leading to biodiversity loss and disrupting the delicate balance of nature.
Deforestation and Resource Depletion: The Unsustainable Cost
The demand for raw materials, like cotton and synthetic fibers, often leads to unsustainable practices like deforestation and resource depletion. Large-scale cotton farming often requires significant amounts of water and pesticides, impacting local ecosystems. The extraction and processing of synthetic materials also consume vast amounts of energy and resources, contributing to environmental degradation and jeopardizing the availability of these crucial resources for future generations. This unsustainable resource use is a critical component of the environmental burden of fast fashion.
Moving Towards a More Responsible Fashion Future
Embracing Sustainable Practices
Sustainable practices are crucial for mitigating the environmental impact of our actions. Implementing eco-friendly initiatives in our daily lives and professional spheres is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. These practices encompass a wide range of activities, from reducing waste to conserving energy and promoting responsible resource management. Transitioning towards a sustainable future requires a collective effort, and each individual plays a vital role in this transformation.
By embracing renewable energy sources, minimizing our carbon footprint, and promoting responsible consumption, we can pave the way for a healthier planet for generations to come. Encouraging sustainable choices in our communities and supporting businesses committed to environmental stewardship are essential steps in this journey.
Promoting Ethical Consumption
Ethical consumption goes beyond simply purchasing products; it involves understanding the entire supply chain. Consumers need to be more aware of the environmental and social impact of their choices. By prioritizing products made with sustainable materials, supporting fair trade practices, and avoiding products with unethical origins, we can drive positive change.
This extends to supporting businesses that prioritize ethical labor practices, fair wages, and safe working conditions. Making conscious consumer choices is a powerful tool for promoting ethical production and responsible business practices.
Prioritizing Transparency and Accountability
Transparency in business practices is essential for building trust and fostering accountability. Companies must be open about their environmental and social impact, disclosing information about their supply chains, production processes, and waste management strategies.
Fostering Collaboration and Partnerships
Collaboration and partnerships play a vital role in achieving a more responsible future. Government agencies, businesses, and NGOs must work together to develop and implement effective strategies for environmental protection, social equity, and economic sustainability. This collaborative approach fosters innovation and accelerates the pace of progress.
Investing in Education and Awareness
Education and awareness are critical for fostering a culture of responsibility. Raising public awareness about environmental issues, ethical consumption, and social justice is crucial for encouraging sustainable practices. Educational initiatives can empower individuals to make informed decisions and actively participate in creating a more responsible future.
Encouraging Innovation and Technological Advancement
Innovation and technological advancements are key drivers of progress toward a more responsible future. Developing and implementing sustainable technologies, such as renewable energy sources, efficient transportation systems, and waste management solutions, is crucial for mitigating environmental impact. Investing in research and development of these technologies is essential for creating a more sustainable future.
Enhancing Global Cooperation
Global cooperation is essential for addressing global challenges like climate change, resource depletion, and social inequality. International collaborations and agreements can establish shared standards, promote best practices, and facilitate the exchange of knowledge and resources. This global cooperation is crucial for achieving lasting positive change across the globe.