Policy and Incentives for Circularity in Fashion
Understanding Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) represents a policy framework that assigns environmental accountability for products throughout their entire existence to manufacturers. Rather than placing waste management burdens solely on consumers or municipalities, EPR encourages producers to integrate sustainability into all product development stages. This forward-thinking approach promotes environmental stewardship by motivating manufacturers to create recyclable designs, minimize packaging, and develop effective disposal solutions.
At its core, EPR establishes manufacturer accountability for environmental consequences. This comprehensive responsibility drives innovation in sustainable design and production methods, extending far beyond simple product creation.
Exploring the Principles of EPR
EPR operates on several fundamental principles that ensure its effectiveness. The producer responsibility principle compels manufacturers to acknowledge and address their products' environmental footprints. This principle encourages sustainable design practices that minimize ecological harm while maximizing resource efficiency.
Product stewardship represents another key principle, fostering responsibility throughout the product lifecycle. This extends beyond basic compliance to active participation in developing sustainable solutions that reduce environmental impact at every stage from conception to disposal.
Delving into the Benefits of EPR
EPR implementation delivers numerous environmental and economic advantages. These policies stimulate innovative product designs that improve sustainability and resource efficiency. Such innovation creates new market opportunities and supports growth in environmentally conscious industries.
Furthermore, EPR facilitates circular economy models where products are designed for extended use, easy repair, and efficient recycling. This approach minimizes waste while optimizing resource utilization, creating more sustainable business practices and resilient communities.
Examining Extended Consumption Responsibility (ECR)
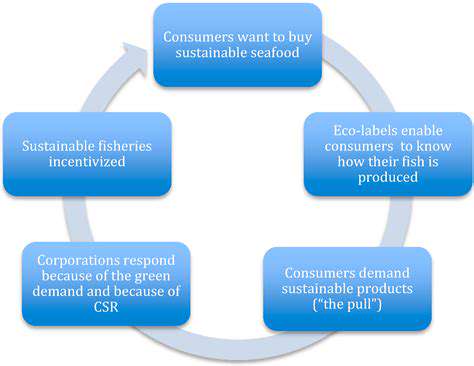
Extended Consumption Responsibility (ECR) complements EPR by focusing on consumer roles in product lifecycles. While EPR emphasizes manufacturer accountability, ECR recognizes consumer influence through purchasing decisions and usage patterns. ECR promotes environmental awareness and provides incentives for sustainable consumption behaviors.
This approach creates a more comprehensive sustainability strategy. By engaging consumers in environmental responsibility, ECR fosters collaborative systems for managing product impacts more effectively.
Comparing and Contrasting EPR and ECR
EPR and ECR represent complementary strategies with distinct focuses. EPR targets producer responsibilities while ECR addresses consumer behaviors. Together they form a comprehensive approach where manufacturers assume environmental accountability while consumers make informed, sustainable choices.
The synergy between these approaches proves essential for creating truly sustainable systems. Collaborative efforts between producers and consumers can establish circular economies that reduce consumption-related environmental impacts, contributing significantly to global sustainability objectives.
The Future of EPR and ECR
EPR and ECR must evolve to address emerging environmental challenges. Incorporating advanced recycling technologies and sustainable materials will keep these frameworks relevant. Continuous adaptation ensures these policies remain effective tools for addressing complex ecological issues.
Growing environmental awareness among consumers increases demand for robust ECR mechanisms. Governments and industries must collaborate to develop programs that support sustainable consumption while equipping consumers with knowledge for environmentally conscious decision-making.
Decentralized metaverse platforms are revolutionizing virtual environment interactions. Unlike corporate-controlled systems, these blockchain-based spaces provide unprecedented control over digital identities and assets. True ownership of virtual existence represents a fundamental shift from current online models. Distributed authority creates more resilient ecosystems where no single entity can arbitrarily change established rules.
Transparency and Traceability: Building Trust and Accountability

Building Trust in Supply Chains
Modern supply chains increasingly rely on transparency and traceability to establish consumer trust. Today's buyers demand clear information about product origins, manufacturing processes, and ethical considerations. Providing this visibility builds consumer confidence and fosters brand loyalty.
This growing transparency demand is transforming supply chain management practices. Businesses are adopting new technologies and processes to enhance operational visibility and ensure accountability across their supply networks.
Enhanced Product Safety and Quality
Advanced traceability systems significantly improve product safety and quality standards. Comprehensive tracking of materials, processes, and locations enables rapid risk identification and corrective action. This proactive approach prevents hazardous products from reaching consumers while maintaining consistent quality throughout supply chains.
Effective traceability allows immediate identification of defective components or contaminated products, enabling prompt recalls. Such responsive systems prove essential in today's interconnected global marketplace.
Improved Regulatory Compliance
Supply chain compliance benefits greatly from transparency systems. These systems provide necessary documentation demonstrating adherence to environmental, labor, and safety regulations. Well-maintained records simplify regulatory audits while reducing compliance risks.
Comprehensive traceability records help businesses meet increasingly stringent regulatory requirements. This supports more sustainable operations while creating predictable, compliant business environments.
Supply Chain Resilience and Agility
Traceability systems enhance supply chain resilience during disruptions. When facing natural disasters or geopolitical instability, businesses can quickly identify affected supply chain segments and implement contingency plans.
This adaptability proves crucial for risk mitigation and operational continuity during crises. The capacity to respond swiftly to challenges ensures long-term business sustainability.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency
Transparency initiatives often yield significant cost savings and efficiency improvements. Identifying supply chain inefficiencies enables process optimization, waste reduction, and logistics streamlining.
Enhanced visibility into inventories, production schedules, and delivery timelines improves forecasting accuracy. This leads to reduced storage costs, fewer delays, and improved profitability.
Ethical Sourcing and Labor Practices
Transparency systems promote ethical sourcing and fair labor practices. Full visibility from raw materials to finished goods helps ensure supply chains remain free from exploitation and environmental harm.
These systems enable greater accountability while empowering consumers to make ethically informed purchases. Such practices support sustainable development and social equity throughout global supply chains.