From Consumer to Activist: Driving Sustainable Change
Understanding the Fundamentals of Collective Action
Collective action, at its core, is the coordinated effort of individuals working together to achieve a shared goal. This shared purpose, whether it's advocating for environmental protection, promoting social justice, or simply improving community living standards, is a powerful force for change. It's about recognizing that individual efforts, while valuable, can be significantly amplified through collective action, creating a ripple effect that extends far beyond the immediate impact of any single person.
Understanding the underlying principles of collective action is crucial. It involves recognizing shared interests, developing strategies for collaboration, and fostering a sense of shared responsibility. This shared understanding and commitment are essential for sustaining the momentum and effectiveness of any collective effort.
The Role of Consumer Activism in Driving Change
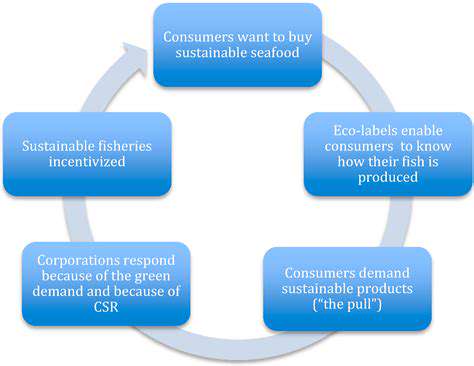
Consumers hold significant power. Their choices, when unified and directed toward specific goals, can pressure businesses and governments to adopt more sustainable practices. From demanding ethical sourcing to advocating for sustainable packaging, consumer activism can drive transformative change in various industries.
By collectively demanding responsible products and practices, consumers can create a market environment that prioritizes sustainability, pushing companies to innovate and adopt more environmentally friendly approaches.
Building Coalitions and Partnerships
Effective collective action often involves building coalitions and partnerships across different sectors and demographics. This collaborative approach allows for the pooling of resources, expertise, and perspectives, ultimately strengthening the collective voice and increasing the impact of the action.
Diverse coalitions can bring together environmental groups, community organizations, businesses, and government agencies. This diverse representation ensures a broader range of perspectives are considered and strategies are tailored to address the complexities of the challenges at hand.
Identifying and Addressing Shared Challenges
One of the most crucial aspects of collective action is the identification of shared challenges. By recognizing common issues, individuals and groups can focus their efforts on solutions that benefit everyone. This shared understanding fosters a sense of community and creates a stronger foundation for long-term change.
Identifying the root causes of problems is equally important. This involves in-depth analysis and research to understand the systemic factors contributing to the issues, enabling the development of targeted and effective solutions.
Strategies for Effective Collaboration
Successful collective action requires well-defined strategies and clear communication channels. This includes establishing clear goals, defining roles and responsibilities, developing a timeline for action, and implementing effective communication strategies to keep all stakeholders informed and engaged. Strong leadership is crucial in guiding and motivating the collective effort.
Transparency and accountability are essential elements of any successful collaboration. Regular updates, open discussions, and mechanisms for addressing concerns ensure that the collective effort remains focused and effective.
Measuring and Evaluating Progress
Monitoring and evaluating the progress of collective action is essential for understanding the impact of efforts and making necessary adjustments. This involves establishing clear metrics, tracking progress over time, and regularly assessing the effectiveness of strategies. Regular feedback and evaluation cycles allow for continuous improvement and adaptation.
By objectively measuring the impact of collective action, organizations can demonstrate the value of their work to stakeholders and attract further support and resources.
Sustaining Momentum and Building a Culture of Change
Collective action is not a one-time event; it's an ongoing process of building momentum, fostering a culture of change, and sustaining engagement over the long term. This requires continuous communication, maintaining a sense of shared purpose, and celebrating milestones to maintain enthusiasm and motivation.
Building a culture of change involves inspiring future generations to embrace sustainable practices and continue the fight for positive change. This is essential for ensuring that the gains achieved through collective action are sustained and expanded in the future.
The Living Building Challenge isn't just about meeting certain standards; it's about embracing a holistic approach to design and construction. This involves a deep understanding of the principles of sustainability, from resource conservation and material selection to minimizing environmental impact throughout the entire building lifecycle. This commitment to ecological responsibility is central to achieving certification, demanding a thorough investigation into local conditions and resources to create a truly sustainable structure.
The Long-Term Vision: Cultivating a Culture of Conscious Consumerism

Understanding the Core Principles of Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture focuses on meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining healthy soil, water conservation, and biodiversity. By integrating eco-friendly practices, farmers can reduce reliance on chemical inputs that harm the environment.
Adopting sustainable principles ensures long-term productivity and ecological balance. This approach encourages crop rotation, organic farming, and responsible resource management. Educating farmers about these core principles is essential for fostering a resilient agricultural system that can withstand climate challenges.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Future Farming Practices
Advancements in technology, such as precision agriculture, drone monitoring, and data analytics, are revolutionizing traditional farming methods. These innovations enable farmers to optimize resource use, reduce waste, and increase crop yields. The integration of smart sensors and AI-driven tools provides real-time insights into field conditions.
Technology not only boosts efficiency but also promotes environmentally conscious decisions. As these tools become more accessible, they will play a crucial role in achieving a sustainable and productive agricultural future, bridging the gap between science and practical farming.
Promoting Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
Biodiversity is vital for maintaining resilient ecosystems that support agriculture. Integrating native plants, encouraging pollinator habitats, and reducing chemical usage help protect vital species and improve crop resilience. Diverse ecosystems can naturally suppress pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
Farmers should prioritize practices that enhance soil health and habitat variety. This not only benefits wildlife but also creates a more sustainable farming environment, ensuring productivity for generations to come.
Implementing Education and Community Engagement
Education programs tailored for farmers, students, and community members are critical in fostering sustainable practices. Workshops, online courses, and field demonstrations can increase awareness and provide practical skills necessary for adopting eco-friendly methods. Community involvement encourages shared responsibility in environmental stewardship.
Building a knowledgeable and engaged community is fundamental for long-term success. Collaboration among stakeholders ensures the development and dissemination of innovative solutions that benefit both agriculture and the environment.
Developing Policy Frameworks for Sustainable Agriculture
Effective policies and incentives are essential to support farmers in transitioning to sustainable practices. Governments can implement subsidies for organic farming, impose regulations to reduce chemical runoff, and promote research into eco-friendly technologies. Policy frameworks should also encourage conservation efforts and land management strategies.
Strong policy support creates an enabling environment where sustainable agriculture can thrive. It aligns economic incentives with environmental goals, ensuring long-term viability and widespread adoption.
Addressing Climate Change and Its Impact on Agriculture
Climate change poses significant challenges to agriculture, including unpredictable weather patterns, droughts, and floods. Developing resilient crop varieties and adopting water-saving irrigation techniques are vital strategies to combat these effects. Farmers must also plan for extreme weather events and diversify their crops to mitigate risks.
Understanding the link between climate change and agriculture is crucial for long-term planning. Proactive adaptation measures can help secure food production and protect livelihoods in a changing climate.