The Journey of a Donated Garment: From You to New Life
Candidate Application Review
The initial phase of the sorting and selection process involves carefully examining every candidate's application. This step aims to pinpoint applicants with the right qualifications and experience for the role. Only those who meet the job description's minimum criteria advance to the next stage. This approach ensures that time and resources are focused on the most promising candidates during later phases.
Rigorous application screening weeds out unsuitable candidates early. This typically includes assessing resumes, cover letters, and other submitted materials. The objective is to find candidates whose skills closely match the position's requirements.
Preliminary Screening Interviews
Candidates who make the shortlist are invited for initial screening interviews. These concise conversations evaluate basic qualifications, job role comprehension, and cultural fit. They serve as an additional filter to identify individuals with potential to thrive in the position.
Conducted via phone or video, these interviews enable broader reach and efficient screening. Their main purpose is to eliminate applicants lacking essential qualifications or whose skills don't align with the role's demands.
Skill Assessments and Tests
To further gauge capabilities, candidates often complete skill assessments. These vary by role but typically measure technical proficiency, problem-solving ability, and job aptitude. This crucial step verifies whether candidates possess the necessary skills for successful job performance.
Technical Interviews
Candidates demonstrating strong potential progress to technical interviews. These in-depth discussions explore technical expertise and practical skill application, focusing on handling job-specific challenges and problem-solving abilities.
Group Discussions and Case Studies
For certain roles, candidates participate in group exercises or case studies. These activities assess communication skills, teamwork, and critical thinking. They reveal how candidates collaborate in teams and approach problem-solving, providing valuable insights into their potential team contributions.
Final Selection and Hiring Decision
The concluding phase involves comprehensive evaluation of each candidate's performance throughout the process. Hiring managers or panels consider skills, experience, cultural fit, and potential. The final decision balances candidate qualifications with organizational needs, culminating in a job offer to the most suitable individual.
The Distribution Network: Connecting Needs with Resources
The Importance of a Robust Distribution Network
An effective distribution network is vital for efficient goods and services delivery. It ensures reliable product access, supporting economic growth and customer satisfaction. Well-designed networks reduce delays and transportation costs, benefiting both businesses and consumers. This infrastructure forms the backbone of successful supply chains.
Inadequate networks hinder market reach, potentially causing lost sales and reduced market share. Consequently, network optimization is essential for long-term business success.
Strategic Location and Infrastructure
Distribution center placement significantly impacts transportation efficiency. Key considerations include proximity to markets, transport hubs, and material sources. Beyond physical location, modern infrastructure like efficient warehouses and transport routes is equally important.
Inventory Management and Control
Proper inventory management maintains ideal stock levels, preventing shortages or excess. It involves demand forecasting, inventory tracking, and proper storage practices. Effective control minimizes storage costs while ensuring product availability.
Accurate demand predictions help businesses optimize stock levels, reducing unnecessary inventory expenses while meeting customer needs.
Transportation and Logistics
Efficient transportation systems form the foundation of distribution networks. Selecting appropriate transport modes (road, rail, air, or sea) depends on cost, speed, and reliability factors. Optimized transportation reduces delivery times and ensures product safety.
Strong logistics management coordinates supply chain stages from order processing to final delivery, including shipment scheduling, tracking, and disruption handling.
Technology Integration and Automation
Technology significantly enhances distribution network efficiency. Advanced software solutions improve inventory management, order processing, and logistics tracking. Automating key operations like order fulfillment reduces errors and streamlines processes.
Customer Service and Delivery Experience
Excellent customer service builds lasting relationships. This includes accurate order fulfillment, clear delivery communication, and effective issue resolution. A smooth delivery experience directly influences customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Distribution networks must prepare for potential disruptions like natural disasters or demand spikes. Contingency plans and risk mitigation ensure business continuity. Backup solutions for transport routes, storage locations, and communication channels minimize unexpected event impacts. Proactive measures substantially reduce disruption consequences.

The Legacy of Giving: A Sustainable Cycle
The Initial Spark: Inspiring the Donation
A donated garment's journey often begins with thoughtful generosity, a wish to make a positive impact. Perhaps an outgrown shirt or unused clothing prompts this giving impulse. This decision frequently stems from environmental awareness and recognition of textile waste issues. The donation act initiates a sustainable cycle that extends beyond the original giver.
Choosing donation over disposal reflects shifting values toward mindful consumption and circular economies. This conscious decision to part with personal items begins the garment's transformative journey, carrying forward the donor's generous spirit.
The Transformation: From Clothing to Resource
Upon reaching charities, recycling centers, or community organizations, donated items undergo transformation. They're sorted, cleaned, and prepared for reuse or repurposing. This careful process involves fabric separation, condition assessment, and suitability determination. The shift from personal belonging to reusable resource maximizes each garment's potential for renewed purpose.
This phase demonstrates the process's interconnected nature. Donor generosity enables the sorting and preparation work, with each step contributing to a more sustainable, circular system.
Reimagined and Renewed: Giving New Life to Textiles
Repurposing opens creative possibilities for donated textiles. From new clothing to home decor, upcycling presents numerous opportunities. This reinvention represents a key moment in the giving legacy, transforming items into valuable resources that continue supporting sustainability.
This stage highlights the ongoing cycle where recipients benefit from donations, simultaneously supporting sustainable fashion systems that prioritize reuse over waste.
The Enduring Impact: A Sustainable Legacy
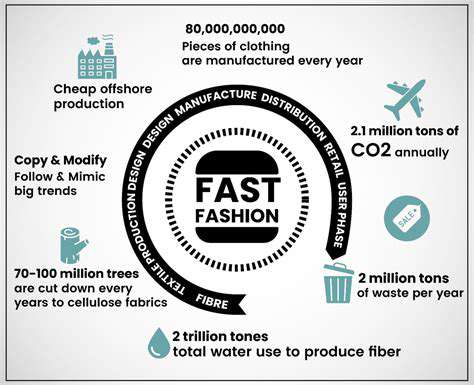
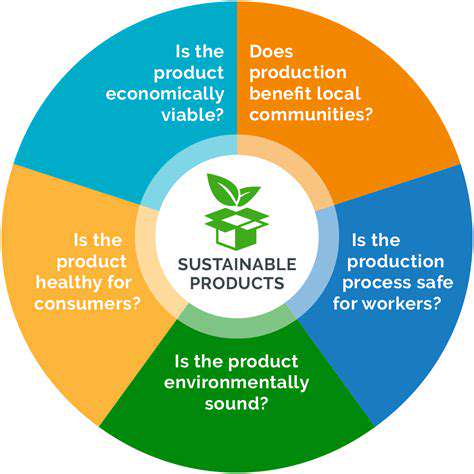
Garment donations reflect broader societal moves toward sustainability. By donating, individuals support circular economies, reduce textile waste, and create new products and opportunities. This impact extends beyond single items, influencing consumption and production patterns.
The giving legacy encompasses both practical resource conservation and the ethical dimensions of sustainable practices, illustrating how individual actions collectively affect environments and communities.