The Global Movement for Sustainable Fashion: Achievements and Next Steps
Extracting Raw Materials: A Critical First Step
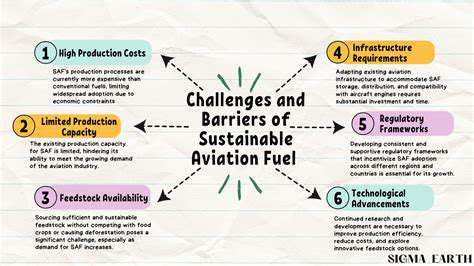
The extraction of raw materials, whether minerals, timber, or agricultural products, is a foundational aspect of our global economy, yet it often comes at a significant environmental cost. The process itself can disrupt ecosystems, leading to habitat loss and biodiversity decline. Furthermore, the energy consumption associated with mining, drilling, and harvesting operations contributes substantially to greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change. Sustainable practices are crucial to minimizing these negative impacts, including responsible sourcing, reducing waste, and implementing environmentally friendly extraction methods.
Manufacturing Processes: Optimizing Efficiency and Minimizing Waste
Manufacturing processes play a pivotal role in transforming raw materials into finished products. However, these processes often generate substantial waste and pollution. Improving efficiency through the implementation of circular economy principles, reducing reliance on harmful chemicals, and adopting cleaner production technologies are essential steps toward minimizing the environmental footprint of manufacturing. Waste reduction strategies, from recycling to innovative waste management solutions, can drastically lessen the environmental burden.
Product Life Cycle: Design for Durability and Sustainability
The design and development of products with a long lifespan and easy recyclability are critical for minimizing environmental impact. Product design should prioritize durability and repairability, extending the product's life cycle and reducing the demand for new materials. Furthermore, the use of recycled and renewable materials in product creation can significantly reduce the environmental strain of resource extraction. This approach fosters a circular economy, where products are designed with their end-of-life in mind.
Consumer Behaviour: Shifting Towards Sustainable Choices
Consumer choices have a profound impact on environmental sustainability. Promoting awareness and education about the environmental implications of product choices is vital. Encouraging the adoption of sustainable consumption patterns, such as reducing consumption, opting for durable goods, and prioritizing products with a lower environmental footprint, can significantly lessen the environmental burden. Encouraging repair and reuse initiatives can also reduce the demand for new products.
Distribution Networks: Optimizing Logistics and Reducing Emissions
Efficient and sustainable distribution networks are crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of product delivery. Optimizing logistics, reducing transportation distances, and leveraging more fuel-efficient modes of transportation, such as electric vehicles, can significantly lessen emissions. Investing in sustainable packaging materials and reducing packaging waste are also important components of a sustainable distribution strategy.
Waste Management and Disposal: Responsible End-of-Life Solutions
Effective waste management and proper disposal are critical for mitigating the environmental impact of products at the end of their life cycle. Implementing comprehensive recycling programs, developing innovative waste-to-energy solutions, and promoting responsible waste disposal practices are vital for reducing landfill waste and minimizing pollution. Moreover, proper disposal procedures ensure that harmful substances are not released into the environment.
Innovation and Technology: Driving Sustainable Solutions
Technological advancements play a critical role in developing innovative solutions to address environmental challenges. Investing in research and development for sustainable materials, waste reduction technologies, and energy-efficient processes is crucial. Supporting innovation in renewable energy sources and promoting technological advancements that minimize waste and pollution are paramount in mitigating the environmental impact of products throughout their entire lifecycle. This includes ongoing development of more sustainable and eco-friendly manufacturing processes.