Collaborative Solutions for Ethical Supply Chains
The Imperative for Collaborative Action
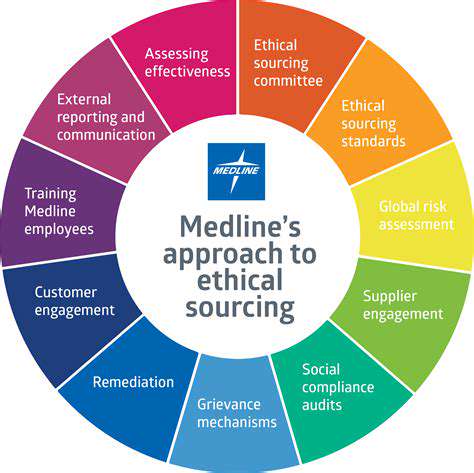
Understanding the Ethical Landscape
In today's interconnected global economy, ethical considerations in supply chains are no longer optional; they are fundamental. Companies face increasing pressure from consumers, investors, and regulatory bodies to demonstrate responsible sourcing practices. This necessitates a shift from a transactional approach to a collaborative one, recognizing the interconnectedness of businesses and their impact on the broader community.
Understanding the intricate web of ethical issues, ranging from labor rights and environmental sustainability to human rights and fair trade practices, is crucial for creating a truly ethical supply chain. This requires a deep dive into the specific challenges and opportunities within each sector, recognizing that diverse industries face unique ethical dilemmas.
The Role of Transparency and Traceability
Transparency and traceability are cornerstones of collaborative action in ethical supply chains. It's not enough to simply declare adherence to ethical standards; businesses must be able to demonstrate their commitment through verifiable data and processes. This includes providing detailed information about the origin of materials, the working conditions in factories, and the environmental impact of production.
Implementing robust traceability systems allows stakeholders to track materials and products throughout the entire supply chain, enabling prompt identification and remediation of ethical violations. This level of transparency fosters trust and accountability, encouraging continuous improvement and ethical practices throughout the chain.
Fostering Collaboration Between Stakeholders
Addressing ethical supply chain challenges requires collaborative efforts from all stakeholders, including producers, manufacturers, retailers, consumers, and governments. Effective communication and information sharing are vital to build trust and foster a shared understanding of ethical responsibilities. This includes actively engaging with suppliers and workers to understand their needs and perspectives.
Collaborative platforms and initiatives can facilitate knowledge sharing, best practice exchange, and joint problem-solving. These platforms can provide a forum for addressing specific ethical issues and developing tailored solutions that work for all involved parties.
Developing and Implementing Ethical Codes of Conduct
Establishing clear and comprehensive codes of conduct is essential for guiding ethical decision-making within a collaborative supply chain. These codes should address all aspects of the supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery. They should be developed collaboratively with input from all stakeholders, ensuring they reflect industry-specific challenges and best practices.
Regular audits and assessments are crucial to monitor compliance with these codes. This enables the identification of areas for improvement and ensures that ethical standards are consistently maintained throughout the supply chain.
Building Capacity for Ethical Practices
Supporting the development of ethical practices throughout the supply chain requires a commitment to building capacity among all stakeholders. This includes providing training and resources to suppliers on ethical labor practices, environmental regulations, and fair trade principles. It also involves promoting a culture of ethical awareness and accountability within organizations.
Investing in education and training programs empowers workers and suppliers to understand and adhere to ethical standards. This fosters a culture of continuous improvement, where ethical considerations are central to all decision-making processes.
Utilizing Technology for Enhanced Monitoring and Auditing
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing the monitoring and auditing of ethical practices in supply chains. Tools like blockchain technology can provide a transparent and secure record of product origins and production processes. This allows for real-time tracking and verification of ethical compliance.
Using data analytics to identify potential ethical risks and trends can help companies proactively address issues before they escalate. This proactive approach ensures that ethical standards are consistently met and that any potential problems are caught early in the process.
Measuring and Reporting on Ethical Performance
Measuring and reporting on ethical performance is critical for demonstrating accountability and driving continuous improvement. This involves establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect adherence to ethical standards, such as labor rights violations, environmental damage, and fair trade practices.
Regular reporting and transparency regarding ethical performance helps build trust with stakeholders and fosters a culture of accountability. This allows for ongoing evaluation and improvement of ethical practices, creating a more sustainable and responsible supply chain for all.
Building Transparency and Traceability

Building Trust Through Transparency
Transparency is paramount in any successful project, particularly in the realm of supply chain management. By openly sharing information about materials, processes, and production locations, organizations can foster trust with consumers, partners, and investors. This open approach builds credibility and allows stakeholders to understand the journey of a product from origin to end-user, ultimately leading to greater confidence and satisfaction.
Transparency in the supply chain allows for greater accountability. When processes are visible, it becomes easier to identify and address potential issues, such as unethical labor practices or environmental concerns. This proactive approach to transparency can prevent crises and foster a more sustainable and ethical business model.
Implementing Traceability Systems
Effective traceability systems are crucial for understanding the origin and movement of materials throughout the supply chain. These systems, often leveraging technology like barcodes and RFID tags, provide a detailed record of each step in the manufacturing process. This detailed tracking allows for a deeper understanding of the product's journey and enables swift identification of potential problems.
Implementing a robust traceability system enhances efficiency and reduces errors. By tracking materials and products, businesses can streamline their operations, minimizing delays and waste. This leads to cost savings and improved overall performance. The data gathered from such systems also provides valuable insights for continuous improvement.
The Benefits of Data-Driven Insights
Data collected through transparency and traceability initiatives provides valuable insights that can be used to optimize operations and improve decision-making. Analyzing this data allows businesses to identify trends, pinpoint areas for improvement, and make informed decisions about resource allocation and process optimization. This data-driven approach allows for proactive problem-solving and increased agility in responding to market changes.
The insights gleaned from transparent and traceable data also contribute to innovation. By understanding the performance of different components and processes, businesses can identify opportunities for improvement and innovation. This can lead to the development of new products, more efficient processes, and increased competitiveness.
Enhancing Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Transparency and traceability are essential for promoting sustainable and ethical practices throughout the supply chain. By making the origins and production processes of products visible, businesses can identify and address potential ethical concerns, such as labor violations or environmental damage. This commitment to ethical practices builds a positive brand image and fosters trust with consumers.
Demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing builds brand loyalty and attracts socially conscious consumers. Organizations that prioritize these values often see a positive impact on their reputation and bottom line. This commitment to transparency and traceability ultimately leads to a more responsible and ethical business model.
Cultivating a Culture of Accountability and Continuous Improvement

Encouraging Ownership and Responsibility
Cultivating a culture of accountability starts with fostering a sense of ownership among team members. When individuals feel personally invested in the success of a project or task, they are more likely to take responsibility for their actions and outcomes. This sense of ownership is crucial for ensuring that everyone understands their role and the impact their work has on the overall goals. It also encourages proactive problem-solving and a willingness to identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
Clear communication of expectations and responsibilities is paramount. By outlining specific roles, deadlines, and performance metrics, individuals can understand the standards against which their work will be measured. This clarity reduces ambiguity and allows for consistent performance evaluations, ultimately creating a more transparent and efficient work environment. Effective communication also fosters trust, a cornerstone of any successful team dynamic.
Establishing Clear Processes and Procedures
Establishing clear processes and procedures for handling tasks and resolving issues is essential for maintaining accountability. Well-defined workflows minimize confusion and ensure that everyone understands the steps involved in completing a task, which reduces the likelihood of errors and delays. This clarity also allows for a more consistent approach to problem-solving, which is critical for maintaining high standards of quality.
Implementing robust documentation systems is another critical element. Detailed records of decisions, actions, and outcomes provide a clear audit trail and facilitate better understanding of past performance. This allows for identification of areas for improvement and ensures that lessons learned are applied to future projects. This documentation also serves as a valuable resource for training new team members and for fostering a shared understanding of best practices.
Promoting Open Communication and Feedback
A culture of accountability thrives on open communication and a willingness to provide and receive constructive feedback. Creating a safe space where team members feel comfortable expressing their opinions, concerns, and suggestions is critical for identifying potential problems early on and fostering a collaborative environment. Open communication allows for a more thorough evaluation of work processes and allows for continuous improvement.
Regular performance reviews and feedback sessions are vital for tracking progress and identifying areas where individuals or teams may need support. These opportunities provide a structured method for acknowledging successes and addressing any challenges, leading to a more productive and engaged workforce. Actively soliciting feedback from all team members fosters a sense of shared responsibility and encourages continuous improvement.