Blockchain for Circularity: Enhancing Traceability: New Applications
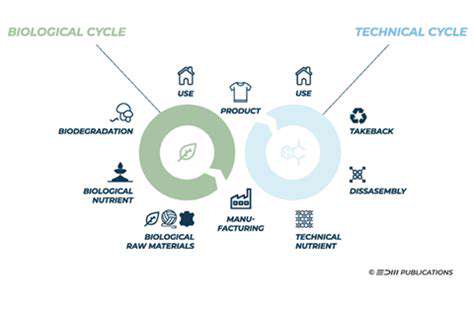
Understanding the Circular Economy
The circular economy represents a radical departure from the outdated linear model of take-make-dispose. Instead, it focuses on maximizing resource efficiency and dramatically reducing waste through innovative approaches to reuse, refurbishment, and recycling. This system keeps materials circulating in the economy for as long as possible, significantly decreasing the environmental burden of production and consumption.
Adopting this model requires nothing less than a complete transformation in how we view product lifespans. Rather than seeing items as disposable, we must recognize their potential for continuous renewal. This paradigm shift demands action from consumers, businesses, and policymakers alike to create the conditions where circular systems can flourish.
The Critical Role of Traceability
At the heart of successful circular systems lies the capacity to monitor materials and products throughout their entire lifecycle. Comprehensive traceability delivers essential information about a product's origins, processing history, and ultimate disposition. This knowledge forms the foundation for optimizing resource use, guaranteeing ethical sourcing, and implementing effective waste management strategies.
Lacking this visibility makes identifying inefficiencies, detecting environmental risks, and ensuring proper disposal nearly impossible. Robust traceability systems aren't merely advantageous - they're absolutely essential for realizing the promise of a genuine circular economy.
Blockchain's Potential for Enhanced Traceability
Blockchain technology, with its unalterable and open ledger system, presents an innovative solution for improving traceability in circular systems. By documenting every phase of a product's journey - from initial extraction to final recycling - blockchain establishes an incorruptible record accessible to all participants.
This unprecedented transparency enables businesses to verify material origins, confirm authenticity, and detect possible contamination issues. The resulting trust among all stakeholders - consumers, companies, and regulators - helps accelerate adoption of circular economy practices across industries.
Implementing Blockchain for Circularity: Challenges and Opportunities
While blockchain offers tremendous potential for improving traceability, practical implementation presents notable hurdles. Incorporating this technology into existing supply chains involves substantial complexity and cost, requiring significant investments in both infrastructure and specialized knowledge. Additionally, achieving standardization and compatibility across different blockchain systems remains an ongoing challenge that must be resolved for smooth data sharing.
However, the potential rewards justify these efforts. By making supply chains more transparent and efficient while building trust among participants, blockchain could become a cornerstone technology for advancing the circular economy. Solving these initial challenges will be crucial for harnessing this technology's full potential in creating a more sustainable future.
Creative problem-solving and strategic partnerships will be vital for overcoming these obstacles and maximizing blockchain's contribution to circular systems.
When fully realized, blockchain's ability to provide comprehensive traceability could empower businesses and consumers alike, paving the way for a more sustainable and durable economic model.
Blockchain: A Transparent and Secure Ledger for Product Journeys

Decentralization and Transparency
Blockchain operates on a distributed network where no single party holds control. This structure promotes complete transparency by recording all transactions across the entire network, making them publicly visible and verifiable. Such openness proves invaluable for establishing trust and accountability, particularly in fields demanding high reliability like supply chain oversight or financial dealings.
The distributed ledger ensures uniform access to information for all participants. This eliminates middlemen and minimizes fraud risks, as any data alteration attempt would be immediately obvious to the whole network. This combination of permanence and transparency positions blockchain as a powerful weapon against corruption while boosting trust across multiple sectors.
Security and Immutability
Blockchain's security stems from sophisticated cryptographic techniques. Each block in the chain receives cryptographic protection, creating an essentially tamper-proof transaction history. The hashing process means any modification would change the block's hash, alerting the entire network to the alteration. This inherent permanence makes blockchain exceptionally reliable for storing and transferring sensitive data.
Blockchain's cryptographic safeguards substantially decrease the likelihood of security breaches, making it ideal for applications where data integrity is critical, such as medical records or financial transactions. The distributed network architecture provides additional protection by spreading risk across numerous nodes.
Applications Across Industries
Blockchain technology continues expanding into diverse fields. In finance, it enables secure international payments while reducing dependence on intermediaries. For supply chains, blockchain offers unprecedented visibility, allowing companies to track goods from source to customer, thereby increasing efficiency and combating counterfeit products.
The technology also shows promise in healthcare for secure medical record sharing and in voting systems for more transparent elections. These varied applications demonstrate blockchain's capacity to transform multiple industries by increasing efficiency, lowering costs, and strengthening security measures.
Smart Contracts and Automation
Smart contracts represent self-executing agreements with terms encoded directly into the blockchain. These automated contracts remove the need for intermediaries while reducing potential disputes. The automation enabled by smart contracts can dramatically streamline processes and cut costs in numerous applications, particularly in contract management where efficient, secure agreement execution is paramount.
Smart contracts also facilitate automated conflict resolution by making contract terms clear and predefined. This eliminates external arbitration needs while significantly reducing the time and resources required to settle disagreements, making the entire process far more efficient. This automation capability represents one of blockchain's most significant advantages.

Beyond Product Traceability: Circularity in Action with Blockchain
Beyond the Basics: Understanding Blockchain's Role in Circularity
While commonly associated with digital currencies, blockchain technology holds far greater potential for sustainability initiatives. Its fundamental strength comes from creating permanent, verifiable records of a product's complete lifecycle from creation to disposal. This level of transparency, exceeding simple tracking capabilities, is essential for optimizing circular systems. By establishing a shared, trustworthy database, blockchain builds confidence among all supply chain participants, including producers, manufacturers, retailers, and consumers.
This improved visibility helps identify inefficiencies and enables better resource distribution throughout the supply chain. It provides comprehensive insight into material flows, which is crucial for developing closed-loop systems and substantially reducing waste. Ultimately, this knowledge facilitates the transition to a truly circular economy where materials are continuously reused, minimizing environmental harm.
Enhanced Transparency and Accountability
Blockchain's most significant contribution to circular systems is its capacity to increase transparency and accountability across entire supply networks. From raw material sourcing to final product disposal, every step is permanently recorded and verified on the blockchain. This transparency empowers consumers to make environmentally conscious purchasing decisions while holding businesses responsible for their sustainability practices.
Streamlining Recycling Processes
Blockchain technology can revolutionize recycling by creating verifiable records of materials moving through recycling systems. This eliminates fraud possibilities while ensuring proper tracking and utilization of recycled materials. Detailed records of material composition and processing steps are vital for maximizing recycled material value and encouraging their reuse in new products. This transparency also enables the development of more efficient recycling operations.
By establishing shared, verifiable recycling records, blockchain fosters cooperation among recycling industry stakeholders, potentially leading to higher recycling rates and reduced environmental impact.
Facilitating Product Take-Back Programs
Blockchain can transform product take-back initiatives by providing secure, transparent systems for collecting, sorting, and processing end-of-life products. Comprehensive tracking enables efficient material monitoring, ensuring proper recycling or reuse of valuable components. This transparency reduces risks of incorrect labeling or material classification that might hinder recycling efforts.
Additionally, blockchain can motivate consumer participation in take-back programs through reward systems, potentially significantly improving material recovery rates when combined with enhanced transparency.
Improving Material Sourcing and Utilization
Blockchain platforms can revolutionize material sourcing by creating centralized databases of available resources. These systems help businesses identify and obtain sustainable materials, reducing dependence on virgin resources and minimizing environmental impact. The technology also supports ethical sourcing by tracking material origins, ensuring fair labor practices and preventing exploitation.
Blockchain's transparency allows companies to verify supplier sustainability claims, encouraging more responsible supply chains that emphasize environmental and social considerations.
Unlocking New Business Models for Circularity
Blockchain technology enables numerous innovative business models supporting circular systems. By creating verifiable product lifecycle records, companies can develop new revenue streams through product resale, reuse, and recycling. This facilitates more sustainable business approaches where products are designed for continuous reuse from the beginning, fostering a more durable economic model.
Blockchain-enabled business models can also incentivize consumer participation in circular processes, encouraging sustainable behaviors like product repair and reuse.