The Role of Brands in Advocating for Recycled Textiles: New Commitments
Innovative Design and Manufacturing Processes: Embracing Recycled Fibres

Innovative Design Strategies
Innovative design strategies are crucial for success in today's competitive market. Companies must consistently push boundaries and explore new approaches to product development. This involves not only developing aesthetically pleasing designs but also focusing on functionality, user experience, and sustainability.
A key aspect of innovative design is understanding user needs. Thorough market research and user testing are essential for creating products that truly meet customer expectations and solve real-world problems. This understanding allows for the creation of products that are not only desirable but also address significant user pain points.
Material Selection and Optimization
Selecting the right materials is fundamental to the success of any manufacturing process. Considerations include cost-effectiveness, durability, and environmental impact. A thorough analysis of various materials and their properties is vital for creating a balanced product design.
Modern manufacturing often utilizes advanced materials with unique properties. These specialized materials can significantly enhance product performance, safety, and longevity. Examples include composites, advanced polymers, and specialized metals.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
Employing advanced manufacturing techniques can dramatically improve efficiency and reduce production costs. These techniques often allow for higher precision and customization, leading to a more tailored product for each customer.
3D printing, CNC machining, and laser cutting are a few examples of advanced manufacturing techniques. These technologies enable complex geometries and intricate designs previously unattainable with traditional methods, opening up new possibilities for product innovation.
Supply Chain Management
Effective supply chain management is essential for streamlined production and timely delivery. A robust and adaptable supply chain allows manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands. This includes building strong relationships with suppliers and having contingency plans for potential disruptions.
Global supply chains present unique challenges, including managing logistics and ensuring compliance with international regulations. Careful consideration of these factors is critical for maintaining the integrity and reliability of the entire manufacturing process.
Quality Control and Assurance
Implementing rigorous quality control measures is paramount for maintaining product consistency and reliability. This ensures that the final product meets the required standards and delivers the expected performance.
Quality control procedures should be implemented throughout the entire manufacturing process, from material sourcing to final assembly. This includes regular testing, inspections, and corrective actions to address any deviations from specifications.
Sustainability Considerations
Sustainability is increasingly important in design and manufacturing. Companies must consider the environmental impact of their products and processes throughout their lifecycle. This includes using recycled materials, minimizing waste, and adopting energy-efficient manufacturing methods.
Sustainable practices are not just good for the environment; they can also enhance brand reputation and attract environmentally conscious consumers. Designing for recyclability and reusability is becoming a critical factor in product development.
Cost Optimization Strategies
Optimizing costs is a key aspect of successful manufacturing. This requires a thorough understanding of all production costs, from raw materials to labor and overhead. Identifying areas for cost reduction without compromising quality is essential for maintaining profitability.
Effective cost optimization strategies can involve process improvements, material substitution, and negotiation with suppliers. Continuous monitoring of costs and proactive identification of cost-saving opportunities are essential for long-term success in the market.
Promoting Circularity and Extended Producer Responsibility
Understanding Circularity
Circular economy principles, at their core, aim to decouple economic activity from the consumption of finite resources. This involves designing products for durability, repairability, and recyclability, extending the lifespan of materials and minimizing waste. A shift towards a circular economy is crucial for mitigating the environmental impact of production and consumption, and brands play a pivotal role in driving this transition.
By embracing circularity, businesses can reduce their reliance on virgin resources, decrease their environmental footprint, and potentially unlock new revenue streams through the reuse and remanufacturing of materials. This approach fosters a more sustainable and resilient future for all.
The Importance of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a crucial component of circularity. It places a significant portion of the responsibility for managing the end-of-life products and packaging of a product on the manufacturer or producer. This encourages them to design for recyclability and consider the environmental impact of their products throughout their entire lifecycle. EPR schemes can incentivize innovation in product design and promote the development of closed-loop systems.
Brand Innovation for Circularity
Brands are increasingly recognizing the importance of integrating circular economy principles into their design and manufacturing processes. This includes developing innovative product designs that are repairable, reusable, or easily recyclable. This proactive approach is vital for achieving significant environmental impact and securing a competitive edge in the market.
Innovative business models, such as product-as-a-service (PaaS) or leasing models, are also becoming increasingly important. These models allow companies to retain ownership of products and materials, enabling them to collect and reuse them at the end of their useful life.
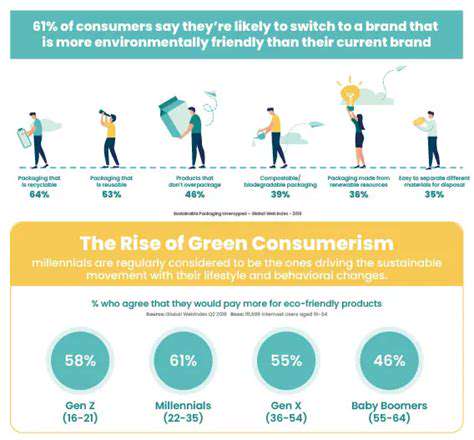
Consumer Engagement in Circularity
Consumer engagement is key to the success of circularity initiatives. Brands need to educate consumers about the importance of responsible consumption and the benefits of choosing products designed for durability and recyclability. Transparency and clear communication about product lifecycle stages and materials used are crucial to fostering consumer trust and participation.
The Economic Benefits of Circularity
Implementing circular economy principles can generate significant economic benefits for brands and consumers alike. Reduced material costs, increased efficiency in resource use, and opportunities for new revenue streams are just some of the potential advantages. These benefits can create a positive feedback loop, incentivizing further innovation and adoption of circular practices.
Government Regulations and Policies
Government regulations and policies play a critical role in shaping the circular economy landscape. Policies that incentivize circular practices, such as EPR schemes or extended warranties, can significantly impact brand behavior and drive the adoption of more sustainable business models. Clearer guidelines and standards for product design and recycling are essential for fostering a collaborative approach to environmental sustainability.
Challenges and Opportunities for Brands
While the transition to circularity presents significant opportunities, brands face challenges in implementing these changes. These include the need for significant upfront investment in new technologies and processes, the need for collaboration with stakeholders, and the complexity of managing material lifecycles throughout the product's entire life cycle. Addressing these challenges effectively will create opportunities for innovation, market leadership, and ultimately, a more sustainable future.