Investing in Circular Fashion Startups: New Opportunities
Designing for Disassembly
A crucial element of circular fashion is designing garments and accessories with disassembly in mind. This involves using readily separable materials, minimizing the use of glued or permanently bonded components, and employing construction techniques that allow for easy material separation at the end of a garment's lifecycle. By enabling the efficient deconstruction of garments, designers can facilitate the recovery and reuse of valuable materials, reducing the reliance on virgin resources and minimizing waste.
This approach not only reduces landfill waste but also opens doors for innovative upcycling processes. Imagine a jacket with zippers and seams strategically placed to allow for the removal of certain components, allowing for the creation of new garments from repurposed fabrics. This forward-thinking design philosophy is essential for creating a truly circular fashion system.
Collaborative Consumption and Sharing Platforms
The fashion industry is ripe for innovative business models that prioritize sharing and rental over ownership. Platforms enabling the sharing of clothing items, from designer dresses to everyday wear, can drastically reduce the number of garments produced annually. This collaborative consumption approach empowers consumers to access a wider variety of styles and brands without the need to constantly purchase new items, reducing demand and minimizing textile waste.
Upcycling and Creative Reuse
Transforming discarded materials into new, desirable products is a cornerstone of the circular fashion movement. The upcycling of existing textiles and garments into new garments or accessories offers a powerful way to breathe new life into waste materials. From transforming old jeans into stylish bags to converting leftover fabrics into unique home décor, the possibilities for creative reuse are vast and hold immense potential for reducing waste and generating income through innovative processes.
Sustainable Materials and Production Processes
Transitioning to sustainable materials and implementing environmentally friendly production processes are paramount in circular fashion. Exploring innovative materials like organic cotton, recycled polyester, and innovative plant-based alternatives is essential. Furthermore, embracing ethical and transparent supply chains, minimizing water usage during production, and reducing the overall environmental footprint of manufacturing are vital steps towards creating a circular fashion ecosystem.
Implementing these practices can significantly reduce the environmental impact of clothing production while also promoting fair labor practices. This commitment to sustainability fosters a responsible approach to fashion production, reducing the industry's reliance on finite resources and minimizing its harmful effects on the planet.
Transparency and Traceability
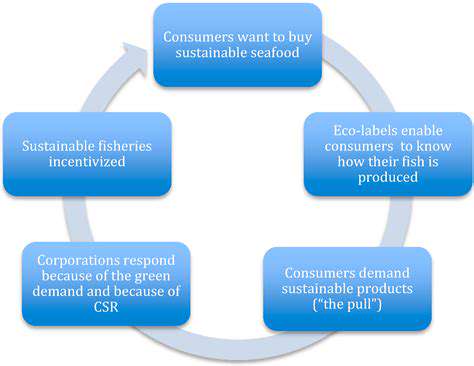
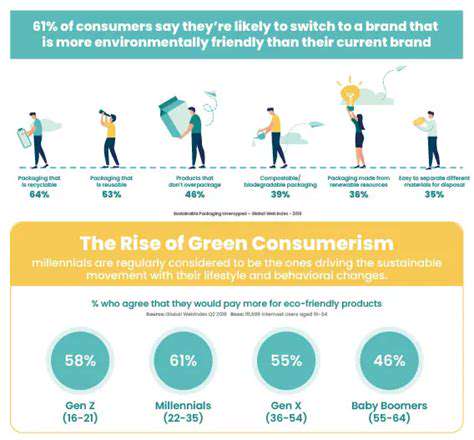
Building trust with consumers is critical in the circular fashion movement. Transparency in the entire supply chain, from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing and distribution, is essential. Consumers need to understand the journey of their clothing items, from origin to end-of-life options. This level of transparency empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions, driving demand for sustainable and ethical practices in the industry.
Implementing robust traceability systems allows brands to track materials and production processes, enabling them to identify and address any potential environmental or social concerns along the way. This proactive approach fosters accountability and builds consumer confidence in the circularity of the fashion industry.
Technological Advancements Driving Circularity
Materials Science Innovations
Advanced materials science is revolutionizing circular fashion by enabling the creation of more sustainable and recyclable fabrics. Researchers are exploring bio-based polymers derived from agricultural waste, mushrooms, and algae, significantly reducing the environmental footprint of textile production. These innovative materials often exhibit superior performance characteristics compared to traditional petroleum-based fibers, offering comfort, durability, and aesthetic appeal while minimizing reliance on finite resources. This shift towards bio-based materials is crucial for decoupling textile production from fossil fuels and fostering a more environmentally conscious fashion industry.
Simultaneously, scientists are developing methods to improve the recyclability of existing synthetic fabrics. Techniques like chemical recycling and mechanical processes are being refined to efficiently break down complex polymers into their constituent monomers, allowing for the creation of new materials from recycled feedstocks. This allows for a closed-loop system, reducing reliance on virgin resources and minimizing waste streams, which is vital for a truly circular fashion model.
Design for Disassembly and Remanufacturing
Circular fashion necessitates a fundamental shift in design principles, moving away from disposable garments to items designed for longevity and recyclability. This involves incorporating modular components and easily detachable elements into garments, allowing for easier disassembly and component reuse. Innovative design approaches prioritize durability and facilitate the process of garment repair and modification, extending the lifespan of clothing items. The incorporation of smart materials and responsive technologies in these designs can further enhance the longevity of the products.
By adopting design principles that prioritize disassembly and remanufacturing, fashion businesses can significantly reduce textile waste and promote the reuse of existing materials. This approach focuses on creating products that can be broken down into their constituent parts and repurposed into new items, minimizing the need for virgin resources and reducing the environmental impact of the fashion industry.
Sustainable Textile Processing Techniques
Traditional textile processing methods often rely on harmful chemicals and energy-intensive processes. Circular fashion advocates for the adoption of sustainable alternatives, such as water-efficient dyeing techniques and the use of natural dyes extracted from plants. These eco-friendly alternatives minimize the environmental impact of textile production while preserving the quality and beauty of the final product. The shift to sustainable processing techniques is critical for reducing the environmental burden of the fashion industry.
Innovative Recycling and Upcycling Technologies
The development of advanced recycling technologies plays a pivotal role in transforming textile waste into valuable resources. These technologies include advanced sorting systems, chemical recycling processes, and innovative upcycling techniques, which transform discarded garments into new products. These solutions are essential for closing the loop in the fashion industry and creating a truly circular system. These technologies, combined with the development of new design strategies, can transform the fashion industry into a more sustainable and environmentally responsible sector.
Digital Technologies for Transparency and Traceability
Digital technologies are revolutionizing the fashion industry by enabling greater transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain. Blockchain technology, for example, can track the origin of materials and the journey of garments from production to consumption, providing consumers with greater insight into the environmental and social impact of their choices. This transparency fosters accountability and promotes ethical and sustainable practices throughout the fashion industry. Moreover, digital platforms can connect consumers directly with designers and manufacturers, facilitating direct-to-consumer sales and reducing waste associated with intermediary retailers.
The Importance of Ethical Considerations
Ethical Sourcing and Production
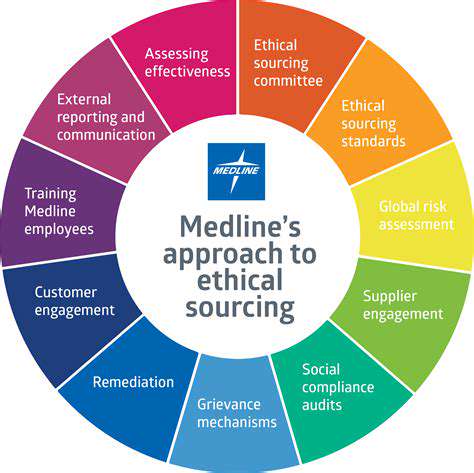
Circular fashion startups often prioritize ethical sourcing, focusing on materials and production processes that minimize environmental impact and promote fair labor practices. This involves working with suppliers who adhere to strict ethical guidelines, ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and responsible resource management throughout the entire supply chain. Choosing a circular fashion startup that places a strong emphasis on ethical sourcing is crucial for investors, aligning their investments with values and contributing to a more sustainable and equitable fashion industry.
Transparency in the supply chain is also a key aspect of ethical sourcing. Investors should scrutinize how startups track and document the origin of their materials, ensuring that they can trace the journey of each component throughout the manufacturing process. This transparency builds trust and allows for accountability, preventing exploitation and promoting responsible practices.
Environmental Impact Mitigation
A significant aspect of circular fashion is its focus on minimizing environmental impact. Startups often employ innovative techniques to reduce waste, conserve resources, and utilize sustainable materials. This could include using recycled or bio-based materials, implementing closed-loop systems for textile recycling, or minimizing water and energy consumption in their production processes. Understanding the environmental footprint of a circular fashion startup is crucial for investors, ensuring they are supporting businesses committed to minimizing their environmental impact.
Investors should also evaluate the startup's commitment to reducing carbon emissions throughout the lifecycle of their products. This includes the energy used in manufacturing, the transportation of materials, and the end-of-life treatment of the garments. Evaluating these factors provides a comprehensive view of a startup's environmental responsibility.
Social Responsibility and Community Impact
Beyond environmental concerns, circular fashion startups often demonstrate a commitment to social responsibility. They may partner with local communities, provide fair wages to workers, and offer opportunities for skill development and empowerment. These initiatives can positively impact the lives of individuals and communities involved in the fashion supply chain. Investors should consider how a startup's social responsibility initiatives contribute to a more equitable and just fashion industry.
Transparency and Accountability
Transparency and accountability are crucial elements of ethical circular fashion. Investors should seek startups that openly communicate their practices, share data on their environmental and social impact, and are willing to be held accountable for their actions. This transparency allows investors to assess the authenticity of a startup's claims and ensure that their investment aligns with their values.
Startups should have clear reporting mechanisms, regularly publishing data on their progress and challenges. This ongoing communication fosters trust and enables stakeholders to understand the impact of the company's actions.
Product Design for Circularity
Investing in circular fashion startups often involves supporting companies committed to designing products with circularity in mind. This includes considering the entire lifecycle of the garment, from its design and production to its end-of-life treatment. Startups may prioritize products that can be easily repaired, reused, or recycled, ensuring that materials remain in use for as long as possible. Understanding how a startup's product design contributes to a circular economy is essential for investors.
Consumer Education and Engagement
Circular fashion startups often play a role in educating consumers about the importance of sustainable practices and the benefits of circular fashion. This could involve creating educational materials, organizing workshops, or providing information on how to care for and extend the life of their garments. By educating consumers, startups promote a shift towards more sustainable consumption patterns. Analyzing a startup's approach to consumer engagement and education helps investors understand the company's long-term strategy for driving adoption of circular fashion.
Navigating the Challenges and Opportunities

Navigating the Complexities of Global Trade
International trade, while offering immense opportunities for economic growth and cultural exchange, presents a multitude of challenges that require careful consideration and strategic planning. Understanding the intricate web of tariffs, regulations, and logistical hurdles is crucial for businesses seeking to succeed in the global marketplace. The ability to navigate these complexities effectively can significantly impact a company's profitability and market position.
Different countries have varying regulations regarding import and export procedures, potentially creating significant obstacles for businesses. These regulations can be complex and time-consuming to decipher, adding to the overall cost and administrative burden of international trade. Thorough research and meticulous adherence to the rules and procedures are vital for avoiding costly errors and delays.
Leveraging Technological Advancements
The rapid advancement of technology has profoundly reshaped the landscape of international trade, offering innovative solutions to traditional challenges. From sophisticated supply chain management software to secure online payment platforms, technological advancements are streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency. Businesses must actively embrace these tools to maintain a competitive edge in the global market.
E-commerce platforms have become increasingly important for businesses seeking to reach global markets. These platforms offer a convenient and cost-effective way to connect with customers across geographical boundaries, expanding market reach and potential revenue streams. These technologies are changing how we do business across borders, and companies that don't adapt may find themselves left behind.
Addressing Cultural Nuances
Successful international trade necessitates a deep understanding of cultural differences. These differences can manifest in communication styles, business etiquette, and even marketing strategies. Businesses must be sensitive to these nuances and adapt their approach accordingly to foster positive relationships and ensure smooth transactions.
Understanding the cultural context of different markets is critical for effective communication and building trust. Failing to consider these factors can lead to misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and ultimately, lost opportunities. Building relationships with local partners who have deep cultural understanding is often essential for success.
Managing Risks and Uncertainties
International trade is inherently fraught with risks, from fluctuating exchange rates to geopolitical instability. These uncertainties can significantly impact profitability and require businesses to develop robust risk management strategies. Identifying potential risks and proactively mitigating them is crucial for long-term success in the global market.
Economic downturns, political instability, and natural disasters are all potential threats to international trade operations. Companies must carefully assess these risks and implement contingency plans to minimize potential damage and ensure business continuity. Developing a comprehensive risk assessment framework and proactive strategies is essential to securing stability in this dynamic environment.