Legal Challenges in User Generated Content Marketing
Copyright infringement is a serious legal issue, impacting creators and industries worldwide. It's a violation of the exclusive rights granted to the copyright holder, which includes the right to reproduce, distribute, display, and perform the work. This infringement can range from unauthorized copying and distribution to the use of copyrighted material in derivative works without permission.
Understanding the different types of copyright infringement and their potential consequences is crucial for both individuals and businesses. Failure to respect copyright laws can result in substantial financial penalties and reputational damage.
Protecting Your Intellectual Property
Protecting your intellectual property is paramount in today's creative landscape. This involves diligently registering your works with the appropriate authorities to establish ownership and enforce your rights. Comprehensive copyright registration ensures that you have a robust legal framework to safeguard your creative output.
Proactive measures, such as employing licensing agreements and watermarking, significantly enhance your ability to prevent unauthorized use of your intellectual property and maintain control over its exploitation.
Fair Use: An Exception to Copyright
The concept of fair use provides a limited exception to copyright law, allowing for the use of copyrighted material without permission in certain circumstances. This exception is typically invoked for educational, critical, or commentary purposes.
However, the application of fair use is complex and depends on a variety of factors, including the purpose and character of the use, the nature of the copyrighted work, the amount and substantiality of the portion used, and the effect of the use upon the potential market for or value of the copyrighted work.
The Importance of Licensing
Licensing agreements are crucial tools for managing the use of your intellectual property. They outline the terms and conditions under which others may use your work, including the scope of permitted use, the duration of the license, and the payment terms. A well-drafted licensing agreement provides a clear legal framework to protect your rights and ensure compliance.
International Copyright Law
Navigating international copyright law is often complex due to variations in legal frameworks across different countries. It's vital to understand the specific copyright laws of the jurisdictions where your work may be used or distributed. This understanding is key to mitigating risks and ensuring compliance with international standards.
Copyright and Digital Media
The rise of digital media has introduced new challenges and complexities to copyright law. Digital distribution platforms and the sharing of content online have expanded the potential for copyright infringement.
Copyright owners and users must adapt to these evolving circumstances and ensure they understand and comply with the copyright laws relevant to digital platforms.
Consequences of Copyright Infringement
The consequences of copyright infringement can be severe, ranging from legal action and financial penalties to reputational damage. Copyright holders have a range of legal options to address infringement, including injunctions, damages, and statutory penalties. It's essential to understand these potential consequences to avoid costly legal battles.
Understanding and respecting copyright laws is crucial for creators, businesses, and individuals alike, to ensure that creativity is protected and that the rights of creators are respected.
Data Privacy and User Consent
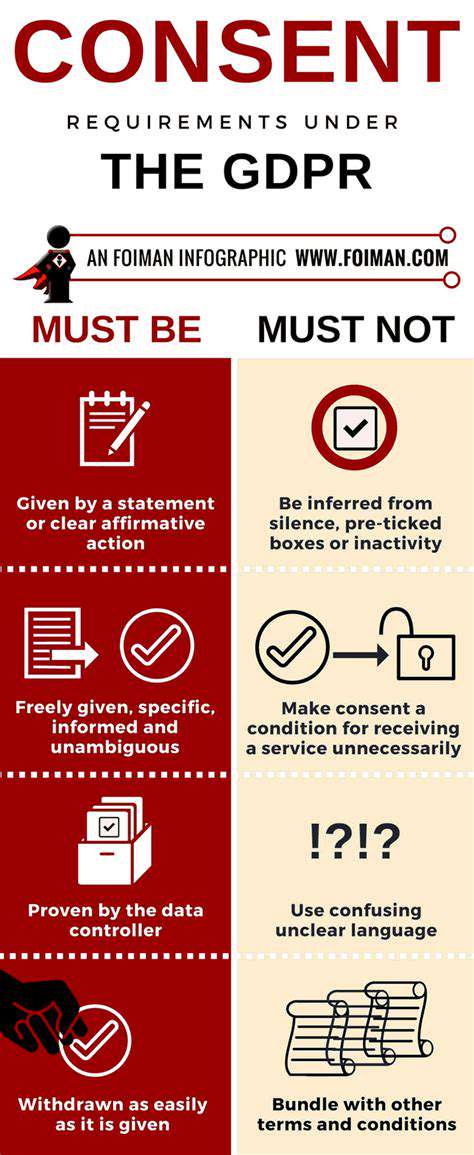
Data Collection Practices
Understanding how your data is collected is crucial for informed consent. Data collection practices encompass a wide range of activities, from passively collecting information about your browsing habits to actively requesting personal details. This includes everything from the websites you visit to the apps you use. These practices are often essential for providing services and experiences tailored to individual needs, but transparency and user control are paramount.
It's important to be aware of the different types of data collected, such as location data, browsing history, and personal information. Knowing precisely what information is being gathered allows users to make more informed decisions about whether or not to provide consent.
Transparency and Disclosure
Clear and concise disclosure of data practices is essential for building trust. Users need to understand what data is being collected, how it will be used, and with whom it may be shared. This disclosure should be readily available and easy to understand, avoiding technical jargon or overly complex language.
Data privacy policies should outline the specific categories of data collected, the purpose for collection, and the recipients of the data. This transparency empowers users to make informed choices about whether to grant consent and how their data will be managed.
User Consent Mechanisms
Effective consent mechanisms are critical for ensuring user control over their data. These mechanisms need to be clear, unambiguous, and easily accessible. Users should not be required to navigate through convoluted processes to understand and grant or withhold consent.
The mechanisms should allow users to easily express their consent or dissent. Options like checkboxes, radio buttons, and clear opt-in/opt-out options should be presented. Using language that is easy to understand avoids potential confusion and empowers users to make informed choices.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with data privacy regulations can lead to significant repercussions, including financial penalties, reputational damage, and legal action. Organizations that fail to adhere to data privacy principles risk significant harm to their bottom line and their brand image. It's crucial to ensure that data privacy practices are robust and compliant with all applicable regulations.
Data breaches can have devastating consequences, exposing sensitive user information and leading to significant financial losses and reputational damage. Implementing strong data security measures and maintaining a robust compliance program are vital steps in mitigating risks associated with non-compliance.
Enforcement and Accountability
Robust enforcement mechanisms and accountability frameworks are critical for ensuring compliance and deterring violations. Effective enforcement mechanisms ensure that data privacy regulations are not just guidelines but are actively upheld. This involves clear processes for reporting violations and resolving disputes.
Organizations should be held accountable for their data handling practices. This accountability creates a culture of responsibility and encourages continuous improvement in data privacy practices. Clear channels for user feedback and redress are essential for maintaining trust and ensuring effective enforcement.
Prefabricated construction is rapidly gaining traction as a viable alternative to traditional building methods. This approach, involving the assembly of pre-manufactured components off-site, offers a multitude of advantages, particularly in the realm of sustainability. By reducing on-site construction time and minimizing waste, prefabrication significantly contributes to a more efficient and environmentally friendly building process. The controlled environment of a factory setting allows for precise material usage and meticulous quality control, further enhancing the overall sustainability of the project.
Dispute Resolution and Contractual Agreements

Dispute Avoidance Strategies
Effective dispute resolution starts before a conflict arises. Proactive measures, such as clear and comprehensive contract language, well-defined roles and responsibilities, and robust communication protocols, can significantly reduce the likelihood of disagreements. Developing strong, mutually beneficial relationships between parties is crucial for fostering trust and collaboration, which are essential for preventing disputes from escalating.
Implementing a system for regular check-ins and progress reviews can help identify potential issues early on. This allows parties to address concerns before they fester and potentially lead to a full-blown dispute. By proactively managing expectations and anticipating potential problems, parties can often avoid costly and time-consuming litigation or arbitration.
Contractual Clauses for Dispute Resolution
Clearly outlining the dispute resolution mechanism within a contract is vital for managing disagreements effectively. This clause should specify the preferred method, whether it be negotiation, mediation, arbitration, or litigation. The clause should also detail the procedures, timelines, and costs associated with each method. Choosing the right clause depends heavily on the nature of the contract and the desired outcome.
Including specific definitions for key terms and conditions, as well as specifying applicable laws and jurisdictions, can help to minimize ambiguity and potential conflicts down the line. These details assist in clarifying expectations and responsibilities, thereby reducing the risk of misinterpretations.
Negotiation as a Dispute Resolution Tool
Negotiation is often the first and most cost-effective approach to resolving disputes. It allows parties to work collaboratively to find mutually acceptable solutions. This process encourages open communication and fosters a sense of shared responsibility in finding a resolution.
Negotiation can be conducted directly between the parties or through a mediator. It's a flexible process that can be tailored to the specific needs of the parties involved, making it a valuable tool for achieving a quick and amicable resolution. However, it may not always be successful in achieving a settlement, particularly in cases involving significant emotional or financial stakes.
Mediation: A Facilitated Approach
Mediation involves a neutral third party – a mediator – who facilitates communication and negotiation between the disputing parties. The mediator helps the parties identify common ground, explore options, and reach a mutually agreeable solution. Mediation is often a more collaborative and less confrontational process than litigation or arbitration. It preserves relationships and often leads to a more creative and tailored outcome.
Arbitration: A Binding Decision-Making Process
Arbitration is a private dispute resolution process in which an impartial arbitrator hears evidence and arguments from both sides and makes a binding decision. This process is often faster and less expensive than traditional litigation. Arbitration provides a more efficient and streamlined method of resolving disputes than court proceedings.
The arbitrator's decision is legally binding, which can be a significant benefit for parties seeking a final and conclusive resolution. However, the decision is usually final and not subject to appeal, so choosing an arbitrator with expertise in the relevant area is crucial for a fair outcome.
Litigation: The Formal Legal Approach
Litigation is the formal legal process of resolving disputes in court. It involves filing pleadings, conducting discovery, presenting evidence, and ultimately having a judge or jury determine the outcome. This option is generally more time-consuming and expensive than other dispute resolution methods. Litigation can be lengthy and complex, potentially straining relationships between the parties.
Litigation is often necessary when the parties are unable to reach a settlement through other means. It provides a structured process for resolving disputes under the law, however, it might not always be the most practical or effective approach, particularly when maintaining a positive relationship is important.