The Future of Ethical Consumption in Fashion: New Predictions
Understanding Transparency in Ethical Supply Chains
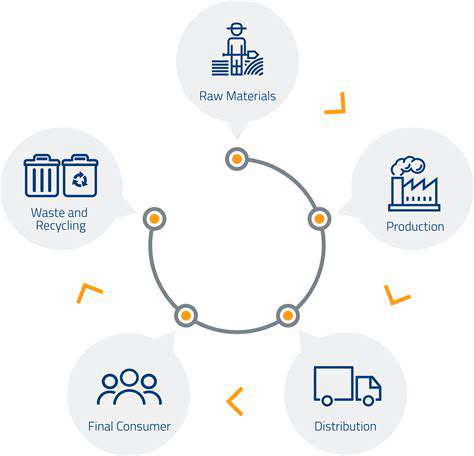
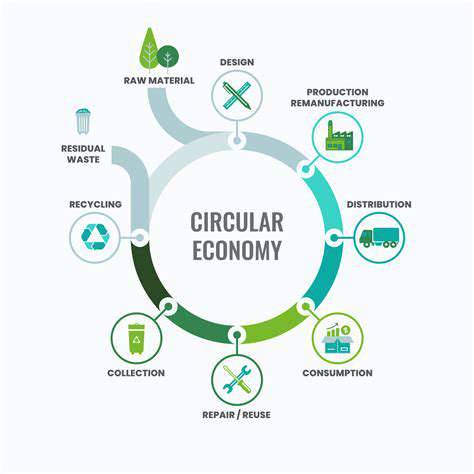
Transparency, in ethical supply chains, means tracking a product’s journey from start to finish. This involves openly sharing details about materials, manufacturing, and labor conditions at every step. It’s not just a trend—it’s a cornerstone of trust, helping consumers and stakeholders grasp the ethical impact of their purchases.
A transparent supply chain encourages accountability, making it easier to spot and fix ethical lapses. This clarity also lets buyers align their spending with their values, backing brands that prioritize ethics.
Traceability: The Key to Verification
Traceability supports transparency by enabling detailed product tracking. Technologies like blockchain or unique IDs document each supply chain step, creating a verifiable record. This digital trail confirms claims about ethical sourcing, fair labor, and sustainability.
Traceability isn’t just about history—it’s a tool for progress. By knowing a product’s origins, companies can pinpoint improvements and risks, fostering a fairer, greener supply chain.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Transparency
New tech is revolutionizing transparency and traceability. Blockchain, for instance, creates unchangeable records of every supply chain move, offering a trustworthy audit trail. This doesn’t just ensure openness—it builds stakeholder confidence.
GPS and sensors add real-time data on goods’ locations and conditions during transit. This granular detail allows quick fixes and upholds ethical standards across the entire process.
Promoting Ethical Labor Practices Through Visibility
Transparency and traceability are vital for fair labor practices. Revealing working conditions, wages, and rights shows a company’s commitment to worker dignity. This openness lets workers report issues and fosters respect.
Transparency also enables audits to verify compliance with labor standards. This accountability is key to preventing exploitation and ensuring safe workplaces.
Building Consumer Trust and Confidence
Today’s buyers demand transparency and traceability. By proving ethical sourcing, brands earn trust and loyalty. This isn’t just about rules—it’s about connecting with consumers who value ethics.
Brands that showcase ethical practices attract support from conscious shoppers, strengthening their reputation.
The Impact on Supply Chain Resilience
Transparency and traceability boost supply chain resilience. Clear visibility into stages and players helps companies anticipate risks like sourcing hiccups or labor disputes. This proactive stance minimizes disruptions.
A resilient, transparent supply chain weathers global uncertainties, benefiting both businesses and communities.
Measuring and Monitoring Progress: Key Performance Indicators
Tracking transparency and traceability requires clear KPIs. Metrics might include ethical supplier compliance, resolved labor violations, or reduced environmental harm. These indicators prove commitment and gauge success.
Ongoing KPI monitoring ensures continuous improvement and alignment with evolving ethical standards.
The Impact of Technology: Revolutionizing Design and Production
The Rise of AI-Powered Design Tools
AI is reshaping design with unmatched automation. Tools generate variations, optimize layouts, and even draft concepts independently. This speeds up creativity but raises questions about human roles and ethics. AI’s trend analysis also predicts design preferences, aiding decisions.
Streamlining Production Processes
Tech like 3D printing and robotics cuts costs and boosts efficiency. Automation reduces manual labor but sparks debates about job losses. Proactive retraining can ease this shift.
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
Cloud platforms and video calls connect global teams in real time. This inclusivity fosters diverse, equitable design processes.
Ethical Considerations in Design Automation
AI’s growing role demands ethical scrutiny. Issues like copyright, bias, and creativity’s future need transparency and guidelines.
Sustainability through Technological Innovation
Tech enables greener production. 3D printing minimizes waste, while recycled materials curb environmental harm.
The Future of Human Creativity in a Technological World
Human creativity remains irreplaceable. Tech amplifies—not replaces—designers’ vision, blending innovation with ethics for a better future.