The Benefits of Extended Producer Responsibility in the Fashion Industry: New Opportunities

Unlocking the Potential of EPR for Fashion

Understanding EPR's Core Principles
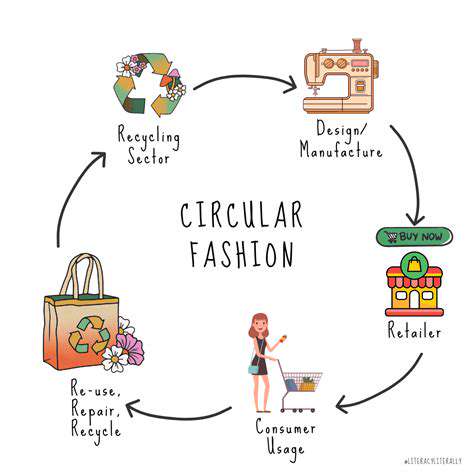
Electronic Product Return (EPR) programs are designed to manage the end-of-life products and components in an environmentally responsible and economically sound manner. At its core, EPR fosters a circular economy, aiming to minimize waste and maximize resource recovery. This crucial aspect of sustainability is driving a significant shift in product lifecycle management. Understanding the fundamental principles of EPR is critical to developing effective strategies for implementation.
These programs typically involve producers taking responsibility for the end-of-life management of their products. This responsibility often includes financial contributions, the development of take-back systems, and the design for disassembly and recycling. A thorough understanding of these core principles is essential for companies to effectively participate in and benefit from EPR.
Designing Effective EPR Programs
Designing a successful EPR program requires careful consideration of various factors, including the product's characteristics, the market context, and the regulatory environment. A key aspect of program design is identifying the most suitable collection and processing methods for the specific products involved. This process involves careful planning and analysis to ensure efficient and cost-effective operations.
Furthermore, clear communication and transparency are essential to engage stakeholders, including consumers, retailers, and recyclers. Establishing clear guidelines for product take-back and ensuring equitable treatment for all parties involved are vital components of program success. This also includes outlining the financial responsibilities of each party involved.
The Economic Benefits of EPR
Implementing EPR programs can yield significant economic benefits for businesses and society. Increased resource efficiency and the potential for cost savings are key advantages. The ability to recover valuable materials from end-of-life products can lead to substantial cost reductions over time. This includes the cost savings related to raw material procurement and the potential for generating revenue through the sale of recovered materials.
Moreover, EPR programs can create new business opportunities and attract investment in sustainable technologies. The potential for creating jobs in collection, processing, and recycling industries is also a major driver. This can lead to a positive economic impact on communities and stimulate economic growth.
Environmental Impact of EPR Initiatives
EPR initiatives play a crucial role in reducing environmental impact by minimizing waste generation and promoting resource recovery. The ultimate goal is to lessen the environmental footprint of products throughout their lifecycle. Minimizing the environmental impact of products is an increasing priority for businesses worldwide.
By diverting materials from landfills, EPR programs contribute to reducing pollution and conserving natural resources. This approach enhances environmental sustainability and fosters a more circular economy.
Challenges and Considerations in EPR Implementation
Implementing EPR programs presents several challenges, from establishing effective collection systems to managing the complexities of product disassembly and recycling. One key challenge lies in ensuring that collection systems are sufficiently comprehensive and accessible to consumers. Understanding the full scope of these challenges is crucial for successful implementation.
Another crucial element is ensuring the sustainability of the recycling process. Ensuring the environmental quality of the recycling process is crucial to avoid unintended negative consequences.

Improving Waste Management and Resource Efficiency
Improved Waste Reduction through Extended Produce
Extended shelf life for produce, achieved through innovative packaging and preservation techniques, directly impacts waste reduction. By enabling consumers to keep fresh produce longer, retailers can minimize spoilage and reduce the amount of food that ends up in landfills. This translates into significant environmental benefits, conserving resources and reducing the carbon footprint associated with food production and disposal.
Furthermore, extended shelf life allows consumers to plan their meals more effectively, reducing impulse purchases and the subsequent discarding of excess produce. This thoughtful consumption pattern not only saves money but also contributes to a more sustainable approach to food purchasing and consumption.
Enhanced Resource Efficiency in the Supply Chain
Extended shelf life for produce fosters resource efficiency throughout the supply chain. Reduced spoilage means less wasted energy and water during transportation, processing, and storage. This translates into lower operational costs for businesses, enabling them to invest in further sustainability initiatives. The reduced need for replacements in the supply chain also streamlines logistics and ensures that resources aren't unnecessarily depleted.
Efficient use of resources throughout the entire supply chain is essential for environmental protection. Extended produce life offers a significant opportunity to optimize resources and minimize negative environmental impacts.
Consumer Benefits and Increased Consumption
Consumers benefit greatly from extended produce shelf life. Longer-lasting produce allows for more flexible meal planning, reduces the frequency of trips to the grocery store, and reduces the likelihood of food going bad before being consumed. This is particularly valuable for individuals with busy schedules or those living in areas with limited access to fresh produce.
Economic Advantages for Retailers and Producers
Extended shelf life for produce offers significant economic advantages for retailers and producers. Reduced spoilage translates directly into lower losses, increasing profitability. This allows for greater investment in sustainable practices, improved product quality, and potentially lower prices for consumers. Furthermore, the ability to supply produce throughout the year reduces reliance on seasonal harvests, creating a more stable and reliable supply chain.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The environmental impact of extended produce shelf life is undeniable. By reducing food waste, we lessen the strain on landfills, conserve natural resources, and minimize the environmental footprint of the entire food system. This includes reducing the amount of water and energy needed to grow, transport, and store produce, thus contributing to a more sustainable agricultural sector. The reduced reliance on synthetic preservatives and pesticides also enhances environmental health and safety.