The Global Impact of Adopting Circular Business Models
Understanding the Core Principles
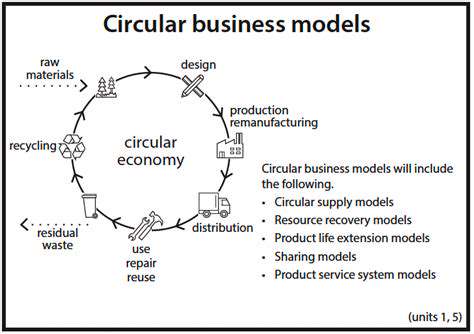
Circular business models represent a significant shift in traditional linear approaches to production and consumption. Instead of the take-make-dispose cycle, these models prioritize resource efficiency, reuse, and regeneration. This fundamental shift is crucial for addressing environmental challenges and creating sustainable economic systems. Circular economy principles aim to minimize waste and maximize the value extracted from materials throughout their lifecycle.
At their core, circular business models focus on designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. This requires a comprehensive understanding of the entire product lifecycle and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Material Recovery and Reuse
A key component of circular business models is the development of innovative approaches to material recovery and reuse. This includes strategies like designing products for disassembly and reuse, implementing closed-loop systems for material recycling, and exploring the potential of innovative technologies for resource recovery. Companies must consider the entire lifecycle of a product, from design to disposal, to ensure that materials are effectively recovered and reused.
Companies are increasingly exploring innovative ways to recapture and reuse materials. This can involve collaborations with other businesses, developing new recycling technologies, and implementing robust supply chain management strategies to ensure that materials are consistently recovered and reused.
Product Lifecycle Management
Circular business models emphasize the importance of managing the entire product lifecycle in a sustainable manner. This includes designing products with durability and repairability in mind, promoting product longevity, and facilitating repair and refurbishment options. Companies are recognizing the value of extending the lifespan of their products, reducing waste, and minimizing environmental impact.
By focusing on the entire lifecycle, from initial design to end-of-life management, circular business models prioritize minimizing waste and maximizing the value of resources throughout the product's existence.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Circular business models often necessitate collaboration and partnerships across different sectors. This includes working with suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders to optimize resource use, promote reuse and recycling, and develop innovative solutions for material recovery and regeneration. Collaboration is key to achieving the goals of a circular economy. Partnerships between businesses, researchers, and governments can lead to significant advancements in sustainable practices.
Companies can learn from each other and share best practices to implement effective circular strategies. This can involve knowledge sharing, joint ventures, and collaborative research efforts.
Economic Benefits of Circularity
Circular business models offer a range of economic benefits, including reduced costs associated with raw materials, waste disposal, and pollution. They also create new business opportunities and stimulate innovation in areas like resource recovery, product design, and service provision. This shift in focus from a linear take-make-dispose model to a circular approach can offer significant long-term cost savings.
By reducing reliance on finite resources and optimizing resource use, circular business models contribute to a more sustainable and resilient economy.
The Role of Technology in Circularity
Technological advancements play a critical role in enabling circular business models. Innovative technologies can improve resource recovery, enhance material recycling, and enable the development of new product designs for durability and reuse. These advancements are crucial for achieving the goals of a circular economy.
From advanced recycling technologies to innovative design strategies, technology is a critical enabler for transforming linear economies into circular ones. This includes advancements in sensors, data analytics, and automation, which can improve efficiency and minimize waste throughout the lifecycle of a product.
Resource Efficiency and Reduced Waste: A Key Driver for Global Impact
Optimizing Resource Utilization
Resource efficiency is paramount to achieving sustainable development goals. By minimizing waste and maximizing the use of available resources, we can significantly reduce our environmental footprint. This involves a holistic approach, encompassing everything from industrial processes to individual consumer choices. Efficient resource management translates into lower costs, reduced pollution, and a more resilient global economy.
Companies and organizations can implement innovative technologies and practices to optimize resource consumption. This includes exploring circular economy models, which promote the reuse and recycling of materials, thereby reducing the need for virgin resources. These strategies not only protect the environment but also foster economic growth by creating new markets and jobs.
Waste Reduction Strategies Across Industries
Waste reduction is a multi-faceted challenge requiring tailored strategies across various industries. For example, in manufacturing, implementing lean manufacturing principles can minimize material waste and optimize production processes. In agriculture, precision farming techniques can enhance resource utilization and reduce pesticide application, promoting environmentally friendly practices.
The food industry, a significant contributor to waste, can benefit from improved supply chain management, reducing food loss and spoilage. Consumer education plays a crucial role in promoting responsible consumption habits. Understanding the lifecycle of products and making conscious choices can drastically reduce waste at the individual level.
Circular Economy Models: A Systemic Approach
The circular economy presents a transformative model for reducing waste and promoting resource efficiency. It focuses on designing out waste, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. This approach moves away from a linear take-make-dispose model to a cyclical one, where resources are reused and recycled.
Implementing circular economy principles requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including businesses, governments, and consumers. By fostering innovation and incentivizing sustainable practices, we can create a more resilient and resource-efficient system.
The Role of Technology in Waste Reduction
Technological advancements play a crucial role in enhancing resource efficiency and reducing waste. Innovative technologies, such as advanced sensors, data analytics, and automation, can optimize resource allocation and minimize waste generation in various sectors. These tools enable precise monitoring and control of resource use, leading to significant improvements in efficiency.
The Economic Benefits of Resource Efficiency
Investing in resource efficiency strategies not only benefits the environment but also yields significant economic advantages. Reduced waste translates into lower costs for businesses, as they spend less on raw materials and waste disposal. This cost savings can be reinvested in innovation and growth, creating a virtuous cycle of economic development and environmental sustainability.
Furthermore, resource efficiency can create new markets and industries focused on sustainable products and services. This fosters economic diversification and job creation, contributing to a more robust and resilient global economy.
Consumer Awareness and Sustainable Consumption
Consumer behavior significantly impacts resource consumption and waste generation. Raising awareness about the environmental consequences of unsustainable consumption patterns is critical. Educating consumers about the importance of responsible choices, such as reducing, reusing, and recycling, empowers them to make a difference.
Promoting sustainable consumption practices, such as opting for products with minimal packaging or supporting businesses committed to environmental responsibility, can collectively contribute to a more sustainable future. Individual actions, when combined, can have a significant impact on reducing waste and promoting resource efficiency on a global scale.
Economic Opportunities and Job Creation: Beyond Environmental Benefits

Economic Growth and Job Creation
Economic growth, fueled by innovation and investment, is a crucial driver of job creation. Businesses expanding into new markets or introducing innovative products and services often require additional personnel to support their growth. This leads to a wider range of job opportunities for individuals with diverse skillsets. Furthermore, government policies that encourage entrepreneurship and small business development can stimulate job creation at the local level.
The creation of new jobs in various sectors, from technology and renewable energy to healthcare and education, is vital for a thriving economy. This necessitates continuous upskilling and reskilling initiatives to equip the workforce with the necessary competencies to meet the demands of the evolving job market.
Industry-Specific Job Opportunities
The growth of specific industries often presents unique job opportunities. For example, the burgeoning renewable energy sector is creating a demand for engineers, technicians, and installers. These jobs offer excellent prospects for individuals with specialized skills in this emerging field. Similarly, the expansion of the healthcare industry is driving a need for nurses, doctors, and other healthcare professionals.
Furthermore, the development of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and robotics, is creating new roles in software development, data analysis, and maintenance. This illustrates the importance of adapting educational programs to meet the evolving demands of the job market.
Skills Gaps and Workforce Development
Despite the abundance of economic opportunities, skill gaps persist in many sectors. This necessitates robust workforce development programs to bridge these gaps and ensure that job seekers possess the necessary qualifications for available roles. Investing in education and training programs can empower individuals to acquire in-demand skills and contribute to the economy effectively. This involves providing access to vocational training, apprenticeships, and continuing education courses.
Moreover, addressing the digital divide and ensuring equitable access to technology and internet connectivity are crucial in equipping individuals with the digital literacy skills needed in today's job market. Targeted initiatives to upskill and reskill the workforce are essential to capitalize on economic opportunities and promote inclusive growth.
Government Policies and Support
Government policies play a significant role in fostering economic opportunities and job creation. Regulations that promote competition, reduce bureaucratic hurdles, and attract foreign investment can stimulate economic activity and job growth. Supporting small businesses through access to capital, mentorship, and training programs can also create job opportunities on a local level. Providing incentives for businesses to invest in local communities is crucial.
Furthermore, policies that encourage innovation and research and development can generate new technologies and industries, leading to novel job creation. Ultimately, creating a favorable business environment is paramount for sustainable job growth.
Transforming Supply Chains: Collaboration and Transparency
Improving Efficiency Through Collaboration
Collaboration across the supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery, is crucial for optimizing efficiency. By fostering strong relationships and open communication between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers, companies can streamline processes, reduce bottlenecks, and minimize waste. This collaborative approach allows for a better understanding of each stage of the supply chain, enabling proactive problem-solving and faster responses to market fluctuations.
Leveraging Technology for Transparency
Modern technology plays a significant role in enhancing supply chain transparency. Real-time tracking systems, data analytics, and blockchain technology provide visibility into every step of the process. This transparency allows stakeholders to monitor product movement, identify potential risks, and ensure ethical and sustainable practices are adhered to throughout the supply chain. Furthermore, improved transparency builds trust and fosters greater accountability.
Building Resilience Through Diversification
Diversifying supply sources and establishing alternative routes can significantly enhance supply chain resilience. Reliance on a single supplier or geographical location makes a supply chain vulnerable to disruptions such as natural disasters, geopolitical instability, or unexpected market shifts. By spreading risk across multiple suppliers and locations, companies can minimize the impact of unforeseen events and maintain uninterrupted operations.
Enhancing Sustainability Practices
Sustainable practices are becoming increasingly important in supply chains. Companies are adopting environmentally friendly manufacturing processes, reducing their carbon footprint, and prioritizing ethical labor standards. This commitment to sustainability not only benefits the environment but also enhances a company's reputation and attracts environmentally conscious consumers. Integrating sustainability into the supply chain fosters long-term value creation and contributes to a more responsible global economy.
Promoting Ethical Sourcing and Labor Practices
Ethical sourcing is a critical component of a responsible supply chain. Companies must ensure that their suppliers adhere to fair labor standards, respect human rights, and avoid exploitative practices. Implementing robust ethical sourcing policies and conducting regular audits throughout the supply chain are essential to maintain ethical standards and uphold a positive brand image. This commitment to ethical practices builds trust with consumers and strengthens the company's reputation.
Fostering Innovation and Adaptability
A dynamic global market demands a supply chain that is adaptable and innovative. Companies must embrace new technologies, explore alternative solutions, and foster a culture of continuous improvement to meet evolving customer demands and stay ahead of the competition. This adaptability allows companies to respond quickly to changing market conditions and ensure long-term success. Innovation and adaptability are essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
Measuring and Monitoring Supply Chain Performance
Effective supply chain management requires rigorous measurement and monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs). Metrics such as delivery time, inventory levels, order fulfillment rates, and customer satisfaction provide valuable insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain. Regular monitoring and analysis enable companies to identify areas for improvement, optimize processes, and make data-driven decisions to enhance performance and achieve greater profitability. By tracking these indicators, companies can identify and mitigate potential risks and ensure the smooth flow of goods and services.
The Global Adoption and Future Outlook: A Multifaceted Approach
Global Trends in Adoption
The global adoption landscape is experiencing a dynamic evolution, driven by diverse factors including changing social norms, economic shifts, and advancements in reproductive technologies. This evolving landscape encompasses a wide array of adoption types, from international adoptions to domestic adoptions and fostering arrangements. Understanding these trends is critical to supporting families and children in need.
Adoption rates are showing fluctuations across different regions, reflecting complex societal influences. This variability necessitates tailored support systems and policies to address the specific needs of adoptive families in various contexts. International adoptions, for example, often face unique legal and logistical hurdles that require careful consideration.
Impact on Family Structures
Adoption significantly alters family structures, creating diverse and resilient family units. These new family configurations often bring unique challenges and rewards, requiring ongoing support and resources for adoptive parents and children alike. The emotional and psychological impact on children adopted from various backgrounds is a crucial area of research and intervention.
Adoptive families often face unique challenges in navigating societal expectations and perceptions. Cultivating a supportive environment that values diversity and fosters open dialogue about adoption is essential for the well-being of all involved.
Economic Considerations
The economic implications of adoption are multifaceted and impact both adoptive families and the broader social system. The financial costs associated with adoption processes, including legal fees, travel expenses, and ongoing support services, can vary significantly depending on the type of adoption and geographic location. These costs can present a barrier for some families seeking to adopt.
The long-term economic contributions of adopted children are complex and require careful consideration. There is a need for comprehensive research and data collection to fully understand the economic impacts of adoption across different demographics and family structures.
Legal and Policy Frameworks
Legal and policy frameworks governing adoption are crucial to ensuring the safety, well-being, and rights of children and adoptive families. These frameworks vary significantly across countries, reflecting diverse cultural values and legal traditions. It is important to consider the ethical implications of adoption policies and their impact on vulnerable populations.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are transforming the adoption process in numerous ways. Online platforms and databases play an increasingly important role in connecting prospective adoptive parents with children in need. These advancements offer opportunities for increased efficiency and access to information, but also raise concerns regarding data privacy and security.
Social and Cultural Perspectives
Social and cultural norms play a significant role in shaping perceptions and attitudes toward adoption. Changing societal views on family structures and the value of diversity are influencing the adoption landscape. Addressing cultural biases and misconceptions related to adoption is essential for creating a more inclusive and supportive environment.
Cultural sensitivity and awareness are critical components of successful adoption processes. Tailoring support services to address the diverse cultural backgrounds of adoptive families and children is crucial for fostering healthy family dynamics.
Future Projections and Research Needs
Future projections for global adoption suggest a continued need for comprehensive research and data collection. Understanding the evolving needs of adoptive families, children, and the broader community is critical for developing effective policies and support systems. Projections also highlight the need for ongoing research into the long-term impacts of adoption on child development and well-being.
Further research into the long-term effects of adoption on children is crucial, particularly on factors such as academic achievement, mental health, and social integration. This knowledge will enable the development of evidence-based interventions to support adoptive families and address any potential challenges.