The Role of Consumers in Driving Circular Design: New Engagement
Understanding the Circular Economy
The circular economy represents a fundamental departure from traditional linear models, focusing instead on maximizing resource efficiency and minimizing waste. By keeping products and materials in use longer, we can significantly reduce environmental harm while extracting greater value from existing resources. This paradigm shift from disposable culture to one emphasizing reuse and regeneration is transforming how consumers interact with products and businesses alike. The collaborative nature of this approach creates new opportunities for sustainable production and consumption patterns.
The Rise of Conscious Consumption
Modern shoppers demonstrate growing awareness of how their purchases affect the environment. With abundant information available and mounting concerns about sustainability, purchasing behaviors are evolving rapidly. People increasingly seek durable, repairable items made ethically rather than cheap disposable alternatives. This mindset shift represents a profound change in consumer values that businesses must acknowledge.
The Impact of Technology on Circularity
Innovative technologies serve as powerful enablers of circular economic models. From 3D printing facilitating custom repairs to advanced recycling methods, these tools help extend product lifecycles significantly. Digital platforms that connect consumers with repair specialists or secondhand markets further accelerate this transition, creating more sustainable material flows throughout the economy.
The Importance of Product Design for Circularity
Thoughtful product design forms the foundation of circular economic success. When manufacturers prioritize durability, repairability and recyclability from the outset, they create products that can have multiple lifecycles. This requires abandoning single-use design philosophies in favor of modular, upgradeable products that can be easily disassembled and repurposed.
Consumer Engagement in Circular Practices
People are increasingly participating in circular economic practices through various means. Many actively seek durable goods, purchase secondhand items, and participate in repair initiatives. This consumer engagement creates powerful market forces that drive demand for sustainable products and services. Sharing economy models have become particularly influential in this transformation.
Business Strategies for a Circular Economy
Forward-thinking companies are adopting circular principles to improve both sustainability and profitability. Innovative approaches like product-as-a-service models and extended producer responsibility programs demonstrate how businesses can benefit while reducing environmental impact. These strategies create economic incentives for companies to consider entire product lifecycles rather than just initial sales.
Policy and Infrastructure Supporting Circularity
Government action plays a crucial role in enabling circular economic transitions. Policies that encourage reuse and recycling, combined with investments in supporting infrastructure, help create the necessary framework for systemic change. Clear regulations regarding product design and lifecycle management can further accelerate this important shift in industrial practices.
The Rise of Conscious Consumption and its Impact

The Shifting Consumer Landscape
Today's consumers demonstrate unprecedented awareness of how their purchases affect society and the environment. This awareness drives significant behavioral changes, transforming shopping from transactional exchanges to value-driven decisions. The growing preference for ethical fashion, fair trade goods and sustainable alternatives clearly reflects this important mindset evolution.
The Impact of Social Media
Digital platforms have amplified consumer voices regarding sustainability issues. Through shared experiences and discussions about ethical consumption, social media fosters collective responsibility. This online discourse powerfully influences purchasing decisions and creates ripple effects throughout markets.
The Importance of Transparency
Modern consumers demand unprecedented visibility into corporate practices, supply chains and production methods. They want assurance that their purchases align with personal values and contribute to positive change. This transparency imperative is forcing companies to operate more openly and accountably.
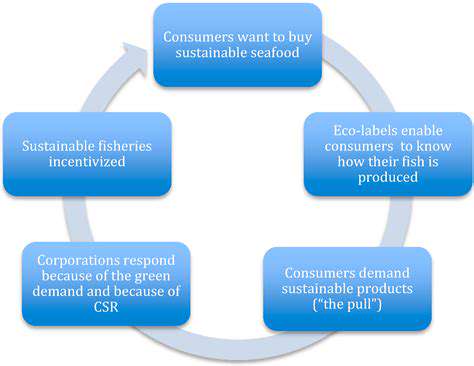
The Role of Sustainability Certifications
Eco-labels and ethical certifications have gained significant importance for conscious consumers. These markers provide crucial guidance, helping shoppers identify products that meet rigorous environmental and social standards. Such certifications build consumer trust in sustainable product claims.
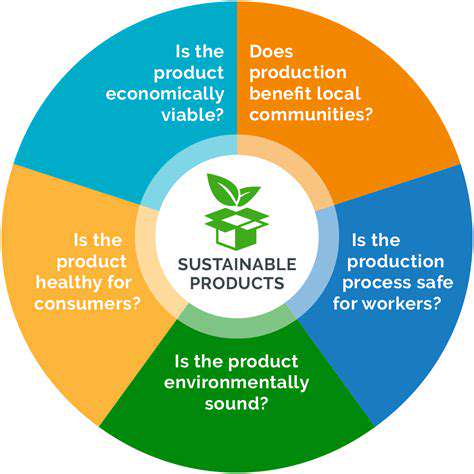
The Rise of Eco-Friendly Alternatives
Demand for sustainable product alternatives continues growing steadily. Consumers increasingly seek biodegradable materials, reduced-impact manufacturing and environmentally responsible packaging. This trend creates exciting opportunities for businesses to innovate with sustainable solutions.
The Growing Influence of Influencer Marketing
Social media influencers play an increasingly important role in promoting sustainable consumption. By showcasing ethical brands and eco-friendly products, these content creators educate audiences and inspire positive behavioral changes. Their reach helps sustainable brands gain visibility among mainstream consumers.
The Future of Conscious Consumption
The conscious consumption movement will continue reshaping retail and supply chains. Companies embracing sustainability and ethical practices will thrive as consumer values increasingly drive purchasing decisions. This transformation is creating a more responsible marketplace where values and commerce intersect meaningfully.
Empowering Consumers through Transparency and Choice
Transparency in Product Information
Comprehensive product transparency empowers consumer decision-making. Detailed information about ingredients, sourcing and manufacturing processes enables shoppers to align purchases with their values. This includes environmental impact data, labor practices and full lifecycle assessments that go beyond basic product specifications. Such transparency builds trust and facilitates truly informed consumer choices.
Choice and Agency in the Marketplace
A diverse product range allows consumers to find options matching their unique needs and values. Marketplaces offering varied formulations, price points and ethical considerations enable meaningful consumer participation in shaping product offerings. Feedback mechanisms like reviews and ratings further empower shoppers to influence market evolution.
Designing for Disassembly and Re-use: A New Paradigm for Product Lifecycle
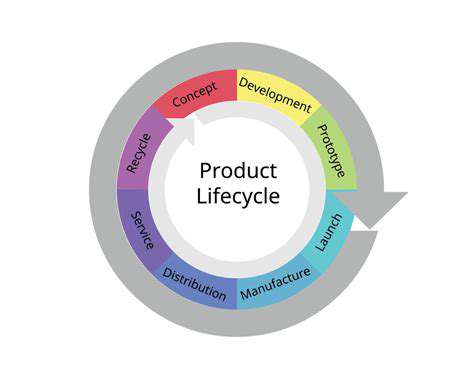
Designing for Disassembly: A Critical Aspect of Product Lifecycle
Disassembly-focused design fundamentally changes how we approach product lifecycles, enabling material recovery and reducing waste. This comprehensive approach considers material selection, component integration and overall structure to facilitate future reuse and recycling.
Material Selection and Compatibility
Choosing easily separable, recyclable materials represents a cornerstone of sustainable design. Material compatibility during disassembly requires careful consideration to ensure efficient recycling processes and prevent contamination.
The Future of Collaboration: Consumers, Businesses, and Policy Makers
The Evolution of Collaborative Tools
Advanced collaboration tools are transforming how teams work together across distances and time zones. Modern platforms enable real-time interaction and simultaneous contribution, breaking down traditional barriers to effective teamwork.
Security and Ethical Considerations
As collaboration becomes more pervasive, robust security measures and ethical frameworks become essential. Protecting sensitive data while ensuring transparent, accountable use of collaborative technologies builds trust in these systems.