Ethical Sourcing and the Pursuit of Fair Wages
Game-based learning leverages our innate desire for recognition. When educators incorporate progress tracking through points, achievement markers, and friendly competition, they tap into powerful motivational psychology. This methodology reimagines learning environments as dynamic spaces where students become active participants in their educational journey. The key lies in balancing motivational elements with substantive learning objectives to create meaningful, lasting engagement.
Environmental Stewardship in Ethical Sourcing

Rethinking Waste
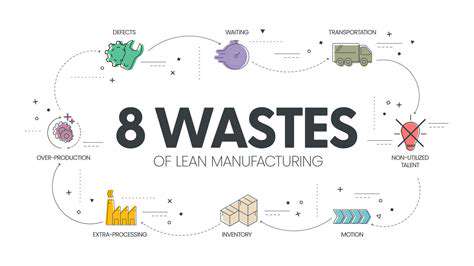
Innovative waste reduction approaches are transforming how businesses view byproducts. The most forward-thinking companies treat waste streams as potential resources, implementing circular systems where materials continuously flow through productive use cycles. This paradigm shift moves beyond traditional recycling to fundamentally redesign production processes with minimal waste as a core objective.
Consumer education plays a crucial role in this transition, helping people understand how proper sorting and disposal of materials enables these circular systems to function effectively. Knowledge empowers consumers to become active participants in sustainable material flows.
The Conscious Consumer Movement
Changing consumption patterns represent one of the most powerful levers for environmental improvement. Shoppers increasingly demand products designed with longevity in mind, favoring items that can be repaired, upgraded, or fully recycled at end-of-life. This market pressure creates powerful incentives for manufacturers to innovate in product design and material selection.
Every purchase decision becomes a vote for a particular vision of the future. By consistently supporting companies with robust environmental commitments, consumers accelerate the transition to sustainable business models across industries.
Biodiversity Conservation
Protecting biological diversity requires multifaceted strategies that address habitat preservation, species protection, and ecosystem restoration. Leading companies now consider biodiversity impact across their entire value chain, from raw material sourcing to product disposal. These comprehensive approaches recognize that healthy ecosystems provide essential services that underpin long-term business viability.
Conservation initiatives must be science-based and locally appropriate to be effective. Successful programs combine habitat protection with community engagement, creating solutions that benefit both nature and people.
Agricultural Innovation
The future of food production lies in systems that work with natural processes rather than against them. Regenerative agricultural techniques rebuild soil health, conserve water resources, and sequester carbon while producing nutritious food. These methods represent a fundamental shift from conventional agriculture's input-intensive approach to a more holistic model.
Supporting local food systems reduces transportation emissions while strengthening community food security. When consumers choose seasonal, locally-grown produce, they support these sustainable agricultural models directly.
Energy Transformation
The shift to renewable energy represents one of the most significant economic transitions of our time. Forward-looking companies aren't just purchasing renewable energy - they're redesigning operations to maximize energy efficiency and minimize overall demand. This comprehensive approach recognizes that the cleanest energy is the energy we don't need to generate in the first place.
Resource Wisdom
In an era of growing resource constraints, efficiency becomes a competitive advantage. Water stewardship initiatives that go beyond simple conservation to address entire watershed health are setting new standards. Similarly, sustainable forestry practices demonstrate how responsible resource management can meet human needs while preserving ecosystems.
The most progressive companies view resource management through a systems lens, recognizing how water, energy, and materials interconnect in complex ways that require integrated solutions.
Cleaning Our Air and Water
Effective pollution control requires addressing sources rather than just symptoms. Industry leaders are adopting clean production methods that prevent pollution at its source through process redesign and material substitution. These prevention-focused approaches prove more effective and economical than traditional end-of-pipe solutions.
Investments in advanced monitoring technologies enable real-time emissions tracking, while innovative treatment methods transform pollutants into useful byproducts. Together, these approaches point toward a future where industrial activity enhances rather than degrades environmental quality.