The Challenges of Ensuring Ethical Production Globally: New Analysis
The Evolving Landscape of Global Supply Chains

The Rise of Global Interconnectedness
Modern society thrives on connections that span continents, with cutting-edge communication and transportation technologies making the world feel smaller than ever. This web of connections enables the seamless exchange of ideas, products, and services across borders, creating remarkable opportunities for joint ventures and economic expansion. However, this intricate network also introduces complex challenges that demand a sophisticated appreciation of diverse cultural frameworks and viewpoints.
The expansion of global trade and foreign investment has allowed companies to grow beyond their domestic markets and explore new territories. Yet this interdependence comes with vulnerabilities – economic instability in one area can trigger cascading effects worldwide. Grasping the interconnected nature of international systems becomes essential for successfully managing these multifaceted relationships.
Technological Disruption and Innovation
Breakthrough technologies are revolutionizing every sector of society at an unprecedented pace. Emerging fields like artificial intelligence, robotic automation, genetic engineering, and clean energy solutions are fundamentally altering our lifestyles, workplaces, and social interactions. These transformations call for adaptability and openness to novel approaches, while simultaneously prompting important discussions about their ethical consequences and societal impact.
The accelerating speed of technological progress presents both advantages and difficulties. Companies must remain innovative to maintain their competitive edge, while workers need to develop skills that match evolving industry requirements. Successfully navigating this dynamic environment demands continuous education and a forward-thinking attitude toward adopting emerging technologies.
Geopolitical Tensions and Shifting Alliances
Contemporary international relations are characterized by changing power structures, regional conflicts, and evolving strategic partnerships. The current geopolitical climate has grown increasingly complicated, necessitating deeper insight into the priorities and ambitions of various nations. These evolving relationships call for skilled diplomacy and a genuine willingness to find mutually beneficial solutions to worldwide issues.
Localized disputes, economic restrictions, and international trade conflicts all contribute to the intricate geopolitical landscape. Comprehending these elements is critical for formulating effective approaches to encourage harmony and security across borders. Constructive international partnerships and open communication remain indispensable for reducing these tensions.
Economic Interdependence and Global Markets
Today's economic systems demonstrate remarkable interconnectivity, with nations depending on each other for manufacturing and distributing products and services. This mutual dependence creates both possibilities and vulnerabilities, as financial instability in one area can produce widespread repercussions. Understanding these complex economic relationships is vital for maintaining financial security and prosperity.
Environmental Sustainability and Global Cooperation
Ecological challenges including climate change and resource scarcity are increasingly acknowledged as collective problems demanding worldwide solutions. Tackling these concerns requires international coordination and dedication to environmentally responsible methods. The global nature of ecological issues highlights the importance of cooperative efforts and shared accountability.
Safeguarding Earth's natural assets and lessening climate change impacts calls for synchronized action from nations, corporations, and citizens everywhere. This demands a fundamental transformation in how we approach progress and resource use, placing greater emphasis on ecological preservation and sustainable practices.
Identifying and Mitigating Risks in Remote Production Sites
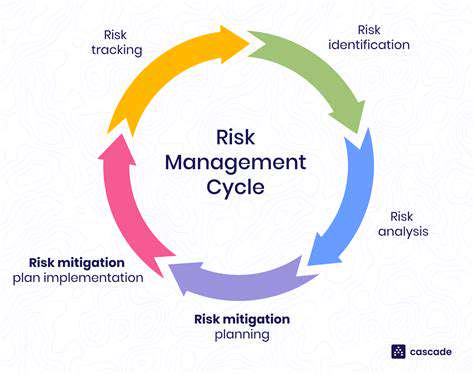
Understanding the Scope of Risks
Recognizing potential hazards forms the foundation of effective risk management. A holistic strategy examines both internal and external elements that might adversely affect project schedules, financial plans, and final results. This encompasses assessing possibilities like supply chain interruptions, economic recessions, or regulatory modifications. Detailed risk evaluations are crucial for pinpointing weak points and formulating protective measures. Clearly defining the risk landscape enables more precise analysis, guaranteeing comprehensive consideration of all pertinent factors.
Evaluating both the probability and potential consequences of various risks represents a critical component of this process. Recognizing the possible severity of threats allows for appropriate prioritization and resource distribution to confront the most pressing concerns initially. For instance, a high-probability, high-impact risk demands urgent focus, while a remote possibility with minimal consequences might justify delayed attention. This analytical approach facilitates optimal resource utilization.
Identifying Internal Risks
Internal vulnerabilities frequently originate from operational shortcomings, improper resource distribution, or communication failures within the company. For example, insufficient expertise in key project areas might cause significant delays or quality issues. Ineffective communication systems can generate confusion and competing priorities, creating project obstacles.
A particularly serious internal threat involves inadequate project management structures. This deficiency can result in ambiguous responsibilities, insufficient progress monitoring, and lack of accountability. Consequently, such situations often lead to squandered time and resources, potentially endangering the entire project.
Assessing External Risks
External threats typically lie beyond organizational control. These dangers may stem from economic conditions, market fluctuations, or broader environmental factors. Financial downturns, shifting consumer trends, or policy adjustments can all influence project results. External variables necessitate vigilant observation and flexibility to maintain project continuity.
Market rivalry and technological progress also represent significant external factors requiring consideration. Adjusting to evolving market requirements and adopting innovative approaches proves essential for maintaining competitiveness. Inability to respond to these external pressures may result in reduced market presence and eventual project termination.
Developing Mitigation Strategies
Following risk identification and evaluation, the subsequent phase involves creating protective measures. These approaches should specifically address particular threats and their possible consequences. This process includes establishing preventive actions, backup plans, and alternative solutions. For example, preparing for potential supply chain interruptions might involve securing secondary suppliers or maintaining reserve inventories. Proactive risk management entails anticipating possible issues and devising solutions before they escalate.
Implementing these protective measures demands full commitment from all participants and unambiguous communication pathways. Ongoing assessment of strategy effectiveness ensures their continued relevance and efficiency. This iterative improvement process proves crucial for adapting to changing threats and preserving project viability.
Implementing and Monitoring Risk Responses
Successful execution of risk mitigation plans requires meticulous preparation and coordination. Clearly defined roles and appropriate resource allocation must be established. Regular progress reports and updates should inform all stakeholders about mitigation efforts.
Monitoring the efficacy of implemented strategies holds equal importance. Periodic evaluations should detect emerging risks or areas requiring strategy adjustments. This cyclical process enables constant refinement and adaptation to shifting conditions, ensuring risk management remains an active and valuable aspect of project achievement.
Addressing Cultural Nuances and Local Regulations
Understanding Cultural Sensitivity
An essential component of ethical business operations involves demonstrating cultural awareness. This means acknowledging and respecting the varied traditions, values, and practices of different societies. Companies operating internationally should refrain from imposing their own cultural standards and instead seek to comprehend and adjust to regional contexts. Neglecting this principle might lead to confusion, offense, and ultimately harm business reputation and relationships.
Cultural awareness extends beyond simple recognition of differences. It requires attentive listening, studying local customs, and modifying communication methods to guarantee respectful and productive exchanges. This includes understanding body language, appropriate forms of address, and even suitable conversation topics in various social situations.
Navigating Local Regulations
Global enterprises encounter intricate networks of regional laws, and compliance represents a fundamental ethical requirement. These legal requirements can differ substantially between countries and sometimes within different areas of the same nation. Failure to adhere to local statutes and regulations may subject businesses to legal consequences, reputational harm, and diminished stakeholder confidence.
Organizations must perform comprehensive research to comprehend and follow all applicable local laws, including employment regulations, environmental policies, consumer protection statutes, and taxation systems. This investigation should remain ongoing, as legal frameworks frequently evolve.
Ethical Sourcing and Labor Practices
Maintaining ethical procurement standards represents a critical priority for internationally operating businesses. This includes carefully choosing suppliers and producers who uphold fair employment standards. Worker exploitation, hazardous conditions, and unfair compensation remain unacceptable and can produce widespread repercussions.
Implementing ethical employment standards involves providing living wages, ensuring safe workplaces, honoring workers' rights, and cultivating positive environments. This necessitates continuous oversight and evaluation of supply networks to verify compliance.
Promoting Fair Competition
Equitable competition stands as a basic tenet of ethical business conduct, particularly in global markets. Companies should avoid anti-competitive practices like price collusion, market division, or exclusionary agreements. Such behaviors can disadvantage consumers, hinder innovation, and create unfair advantages.
Encouraging fair competition requires following antitrust legislation, avoiding deceptive marketing, and respecting intellectual property. Transparency and honest communication represent key components in establishing an ethical competitive landscape.
Addressing Environmental Concerns
Ecological sustainability has become an increasingly prominent consideration in international commerce. Businesses bear responsibility for minimizing environmental harm and operating in ways that protect local ecosystems and resources. This includes reducing pollution, conserving energy, and implementing sustainable operational methods.
Multinational corporations must consider environmental regulations and recommendations in all operational locations, and actively work to mitigate potential ecological damage. This encompasses developing sustainable supply networks and advocating responsible resource utilization.
Respecting Intellectual Property Rights
Protecting intellectual property represents a critical ethical obligation, especially in international contexts. This includes honoring patents, trademarks, copyrights, and proprietary information belonging to others. Intellectual property violations can lead to legal consequences, financial penalties, and reputational harm.
Companies must ensure their operations and products comply with relevant intellectual property laws in all markets. This involves conducting thorough research and obtaining required licenses and authorizations.
Transparency and Accountability
Openness and responsibility form essential components of ethical business behavior in global markets. Clear communication with stakeholders including customers, employees, and local communities remains crucial. This involves providing accurate information about business activities, policies, and procedures.
Organizations must accept responsibility for their decisions and actions, and address stakeholder concerns. Establishing clear feedback mechanisms and dispute resolution processes represents an important aspect of maintaining ethical standards.
The Importance of Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement
Understanding the Value of Collaboration
Successful teamwork proves indispensable for managing the complexities of achieving project objectives. A cooperative methodology fosters mutual understanding of project aims, encourages varied viewpoints, and helps identify and overcome potential obstacles. This shared accountability, when embraced by all participants, generates greater innovation and efficiency, ultimately producing stronger and more meaningful results. Through active interaction, teams can capitalize on each member's distinctive strengths and knowledge, leading to a more thorough and balanced approach.
Additionally, cooperation reduces the likelihood of isolated work environments developing, ensuring project cohesion and alignment with overall goals. This interconnectedness promotes collective ownership, motivating participants to contribute actively and pursue excellence. This unified vision encourages greater openness and clear communication, establishing a constructive and fruitful atmosphere for everyone involved.
Identifying and Engaging Stakeholders
Accurate stakeholder identification remains paramount for any project. This involves recognizing not only directly involved individuals but also those with indirect influence or interest in project outcomes. By understanding varied stakeholder requirements, concerns, and expectations, project leaders can customize communication and involvement approaches to maximize support and minimize potential disagreements. A comprehensive stakeholder analysis establishes the foundation for proactive relationship management, ensuring all participants feel acknowledged and valued throughout the project duration.
Effective stakeholder engagement demands more than simple information sharing. It requires active listening, creating feedback opportunities, and addressing concerns promptly and transparently. Establishing dialogue platforms, whether through scheduled meetings, surveys, or digital forums, allows stakeholders to express opinions and contribute valuable perspectives. This reciprocal communication fosters partnership, demonstrating that their input is respected and appreciated, ultimately strengthening commitment and dedication.
Overcoming Communication Barriers
Clear communication represents the cornerstone of successful teamwork. Precise and concise exchanges help ensure universal understanding, reducing confusion and promoting shared comprehension of project aims. However, communication breakdowns can emerge from various causes, including differing communication preferences, language differences, or insufficient dedicated engagement time. Addressing these challenges proactively remains essential for sustaining project momentum and success.
To overcome these obstacles, project teams should establish clear communication protocols and channels. This might involve implementing regular updates, utilizing collaborative platforms, and ensuring all participants receive necessary information promptly and understandably. Investing in communication training can also equip team members with skills and knowledge to navigate potential communication hurdles, ultimately ensuring smoother and more effective collaboration.
Building Trust and Maintaining Momentum
Trust forms the foundation of any productive partnership. When stakeholders trust the project team and their dedication, they become more likely to participate actively and support project objectives. Establishing trust requires openness, reliability, and demonstrated commitment to agreed timelines and deliverables. Consistent actions and communication reinforce team dependability, creating a positive and efficient working environment.
Sustaining project momentum throughout its duration remains equally critical. This involves proactively addressing challenges, adapting to changing circumstances, and maintaining focus on primary objectives. Regular check-ins, progress updates, and open discussions help preserve momentum and identify potential issues early. Acknowledging and celebrating achievements, both major and minor, further strengthens team commitment and motivation, keeping the project progressing effectively.