From Farm to Factory: Ensuring Ethical Practices in Fashion
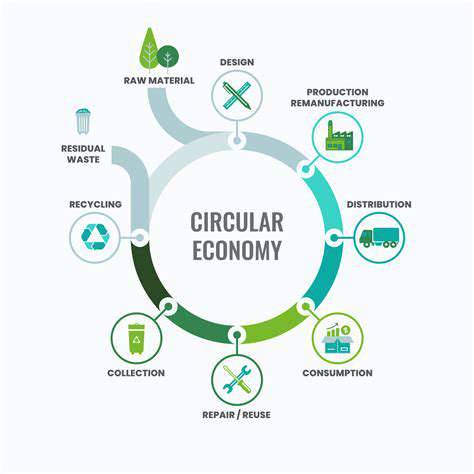
Raw Materials: The Foundation of Fashion
The fashion industry's journey begins long before the clothes hit the runway. From the cotton fields of the American South to the vast tea plantations of Asia, the raw materials that form the basis of our garments undergo a significant transformation. Cultivating these materials requires careful attention to environmental factors, agricultural practices, and even the weather patterns of the growing season. The quality and availability of these raw materials directly impact the final product, influencing everything from the fabric's texture to its durability.
The sourcing of these materials is a complex process, often involving intricate supply chains and partnerships with various farmers and producers. Ethical considerations regarding fair labor practices and sustainable agricultural methods are increasingly important in this stage, as consumers demand greater transparency and accountability throughout the production process.
The Manufacturing Process: Transforming Raw Materials into Garments
Once the raw materials are sourced, the true manufacturing process begins. This phase encompasses a vast array of steps, from spinning fibers to weaving fabrics, and ultimately, sewing the finished garment. The intricate machinery and skilled labor involved in this transformation are often concentrated in specific regions, driven by factors like cost-effectiveness and the availability of specialized expertise.
Modern manufacturing often involves intricate machinery and automated processes, which have drastically changed the landscape of garment production. However, traditional methods still hold significance in certain parts of the world, preserving cultural heritage and unique craftsmanship.
Design and Innovation: Shaping the Future of Fashion
Design plays a pivotal role in the fashion industry, driving innovation and shaping consumer preferences. From runway shows to online platforms, designers constantly experiment with new styles, silhouettes, and materials to create garments that resonate with their target audience. This stage of the process is often influenced by current trends, cultural shifts, and even historical events.
Distribution and Logistics: Moving Garments to Consumers
The transportation and distribution of garments are critical components of the overall fashion production process. From the manufacturing facilities to retail stores and ultimately, consumer homes, these products traverse complex logistical networks. Efficient and sustainable distribution methods are becoming increasingly important as consumers become more aware of the environmental impact of their purchases.
Retail and Consumer Interaction: The Final Mile
Retail plays a crucial role in connecting the garment to the consumer. From high-end boutiques to mass-market stores, the retail environment significantly influences how consumers perceive and interact with clothing. Marketing strategies, store design, and customer service all contribute to the overall consumer experience, shaping purchasing decisions and ultimately, the success of the product.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability in Fashion
The fashion industry's environmental footprint is a significant concern. From water pollution during textile production to carbon emissions from transportation, the industry faces considerable pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. Consumers are increasingly demanding more environmentally conscious choices, driving brands to implement eco-friendly materials, reduce waste, and optimize their supply chains.
Ethical Considerations: Fair Labor Practices and Social Responsibility
Ethical considerations are paramount in the fashion industry. Ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for human rights throughout the entire supply chain is crucial. As consumers become more aware of the social impact of their purchasing decisions, brands are increasingly pressured to adopt ethical sourcing and production strategies, contributing to a more responsible and sustainable industry.

Evaluating brand resonance in virtual worlds transcends simply counting impressions or views. A true understanding requires delving into the emotional and experiential connections users forge with a brand. This involves analyzing how deeply the brand resonates with their identities, aspirations, and values within the virtual environment. Simply put, it's not just about seeing an ad; it's about feeling a connection.