Protecting Migrant Workers in the Fashion Industry: Ethical Imperatives: New Initiatives
Transparency and Accountability
In today's business landscape, being open about operations isn't just good practice—it's an ethical necessity. When companies clearly communicate their sourcing methods, manufacturing processes, and environmental impacts, they build lasting trust with everyone invested in their success. This openness creates a culture where people take responsibility for maintaining high ethical standards. It also invites valuable outside perspectives that can help spot potential issues before they become serious problems.
True accountability goes beyond individual actions. Organizations need strong systems for reviewing ethical practices and reporting concerns. These systems must protect employees who speak up about wrongdoing, ensuring they face no negative consequences for doing the right thing. Effective whistleblower protections create an environment where ethical issues can be addressed constructively.
Fair Labor Practices
Treating workers fairly forms the foundation of ethical business. This means paying living wages, providing safe workplaces, and respecting workers' rights to organize. Forward-thinking companies understand their employees are their most valuable resource, not just another cost. Pay should reflect the value of the work performed, and working conditions must meet or surpass all legal requirements. Building diverse, inclusive teams is equally important for creating fair workplaces.
Businesses must actively combat exploitation throughout their supply chains. Regular supplier audits and collaborative improvement plans help ensure decent working conditions for everyone involved in production.
Environmental Sustainability
Today's businesses can't ignore their environmental responsibilities. Reducing environmental harm through sustainable operations has become non-negotiable. Ethical companies consider the full lifecycle of their products, from raw material sourcing to disposal. They work to minimize waste, conserve resources, and lessen their ecological impact.
Practical steps like switching to renewable energy, cutting carbon emissions, and redesigning packaging show real environmental commitment. These actions don't just help the planet—they often improve efficiency and strengthen brand reputation over time.
Respect for Human Rights
Protecting human rights is fundamental to ethical business. Companies must safeguard these rights at every level of operation, from their own staff to their furthest suppliers. This includes ensuring freedom from discrimination and the right to organize. Proactive measures are needed to prevent any involvement in human rights violations, requiring thorough vetting and ongoing oversight of business partners.
Ethical businesses also support human rights in their communities. This might mean funding local education programs, backing social initiatives, or partnering with advocacy groups to address pressing issues.
Product Safety and Quality
Selling safe, high-quality products is a basic ethical obligation. Responsible companies test products thoroughly at every production stage, using safe materials and providing clear usage instructions. Proper labeling and honest product claims are equally important.
When concerns arise, companies should respond quickly and effectively. Maintaining open communication channels builds consumer trust and demonstrates commitment to customer wellbeing.
Ethical Marketing and Advertising
Honest marketing builds lasting customer relationships. Companies should avoid misleading claims and ensure all advertising reflects reality. Responsible marketing means not taking advantage of vulnerable groups and following all relevant regulations.
Cultural sensitivity matters too. Marketing should avoid stereotypes and promote positive social values through thoughtful language, imagery, and audience targeting.
Corporate Social Responsibility
True corporate responsibility extends beyond profit. Ethical companies integrate social and environmental considerations throughout their operations. Their CSR programs might include charitable giving, community projects, or conservation efforts—all contributing to broader societal good.
Well-designed CSR initiatives create mutual benefits, enhancing company reputation while making meaningful differences in communities.

Combating Modern Slavery and Human Trafficking in Fashion Production
Understanding the Scope of the Problem
Behind fashion's glamorous facade often lies a grim reality of exploitation. From forced labor in cotton fields to trafficked workers in garment factories, this global industry has serious human rights challenges. The problem spans entire supply chains, with vulnerable people suffering while brands and consumers remain unaware. Tackling these issues requires understanding how complex production networks can hide abusive practices.
Global production makes measuring the problem difficult, but investigations consistently reveal forced labor and other abuses. Opaque supply chains and dangerous working conditions allow exploitation to continue unchecked, with workers often unable to report violations safely.
Addressing the Systemic Issues
Fighting fashion-related exploitation demands comprehensive solutions. Brands must increase supply chain transparency through rigorous supplier audits and monitoring systems. Worker empowerment is equally crucial—ensuring fair pay, safe conditions, and the right to organize without fear.
Supporting worker advocacy groups and providing legal protections helps create systems where abuses can be reported and addressed properly.
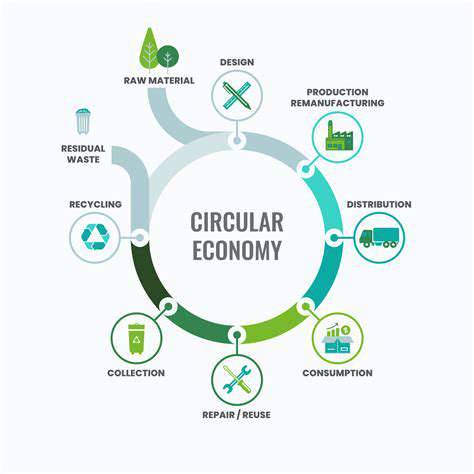
Promoting Ethical and Sustainable Practices
The industry must fundamentally shift from profit-first thinking to ethical responsibility. Consumers drive change by supporting brands with transparent, ethical supply chains. Sustainable materials, waste reduction, and fair trade principles can transform the industry while protecting workers.
Circular business models offer environmental benefits while creating fairer working conditions. This holistic approach can build a fashion industry that respects both people and planet.