Sustainable Fashion Trends You Need to Know for 2026
Circular Design and the Rise of Upcycling
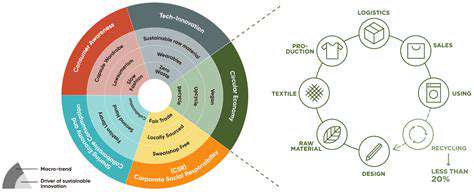
Circular Design Principles
Circular design, a key concept in sustainable development, focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization throughout a product's lifecycle. It encompasses a range of strategies, from designing products for disassembly and reuse to promoting the sharing economy and encouraging responsible consumption habits. This approach seeks to move away from a linear take-make-dispose model, which often leads to environmental damage and resource depletion.
By understanding the entire life cycle of a product, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, circular design aims to create a more sustainable and resilient system. This holistic perspective allows for the identification of opportunities for improvement and innovation at every stage.
The Importance of Material Selection
Choosing sustainable and recyclable materials is crucial in circular design. Materials with a lower environmental impact and a higher recyclability rate are preferred over those that are difficult to recycle or contribute significantly to pollution during manufacturing. Using recycled content in new products is another important strategy. This reduces the need for virgin resources and minimizes the environmental footprint.
Considering the entire lifecycle of the material, from extraction to disposal, is essential. The environmental impact of different materials and their potential for reuse or recycling should be carefully weighed during the selection process.
Product Design for Disassembly and Reuse
Designing products with disassembly in mind allows for easier component separation and reuse. Modular designs, where components can be easily detached and reconfigured, are particularly beneficial. This approach facilitates the recovery of valuable materials and reduces the need for new material extraction.
Promoting the Sharing Economy
The sharing economy plays a significant role in reducing the need for individual ownership and promoting resource efficiency. Platforms that facilitate the sharing of products and services can minimize the production and consumption of new items, thereby reducing environmental impact.
Sharing models can extend the lifespan of products, reducing waste and promoting a more sustainable consumption pattern. This concept can be applied to a wide range of products, from cars and tools to clothing and equipment.
The Role of End-of-Life Management
Effective end-of-life management strategies are essential for circular design. Designing products that can be easily disassembled, recycled, or composted is vital for minimizing waste and maximizing resource recovery. Companies should actively engage in the development and implementation of recycling systems to ensure that materials can be effectively reused.
Properly managing end-of-life products reduces the environmental burden associated with landfills and incineration.
Consumer Education and Awareness
Raising consumer awareness about the importance of circular design principles is critical for driving change. Educating consumers about the environmental impact of their choices and promoting responsible consumption habits are essential for creating a more sustainable future.
Encouraging consumers to prioritize products designed for durability, repairability, and recyclability will have a significant impact on the overall system.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
Technological advancements and innovations play a significant role in enhancing circular design practices. Developments in recycling technologies, material science, and product design tools can help improve the efficiency of resource utilization and minimize waste generation.
Investing in research and development to improve recycling processes and create new sustainable materials is crucial for the future of circular design. This includes the development of bio-based materials and improved methods for separating and recovering valuable materials.
Ethically Sourced Materials and Transparency
Ethical Sourcing of Fabrics
Sustainable fashion isn't just about stylish clothes; it's about the journey those clothes take from raw material to finished product. Ethical sourcing prioritizes fair labor practices throughout the supply chain. This means ensuring workers receive fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for their human rights. It extends beyond the factory floor to encompass the sourcing of raw materials, including cotton, wool, and silk, looking for certifications and practices that minimize environmental impact, such as organic farming and responsible harvesting. Choosing ethically sourced fabrics is a crucial step toward a more sustainable and responsible fashion industry.
Transparency in the supply chain is key to ethical sourcing. Consumers deserve to know the story behind the clothes they wear. Knowing where the fabric comes from, how it's produced, and the conditions under which it was made empowers consumers to make conscious choices aligned with their values. This transparency fosters accountability and encourages brands to adopt more ethical and sustainable practices.
Transparency in Manufacturing Processes
Understanding the entire production process, from initial material selection to final product delivery, is vital for ethical sourcing. This includes examining working conditions in factories, ensuring fair wages and safe environments for workers, and minimizing the environmental footprint of manufacturing processes. Transparency in manufacturing allows consumers to assess the overall impact of their purchases on people and the planet, promoting accountability and driving positive change.
Detailed information about the manufacturing process, including the use of specific chemicals, water usage, and energy consumption, should be readily accessible. By providing this detailed information, companies empower consumers to make informed decisions and hold themselves accountable for their environmental impact.
Animal Welfare in Textiles
For fabrics derived from animals, like wool and leather, ethical sourcing extends to the treatment of the animals. Consumers are increasingly aware of the importance of humane practices in animal agriculture. This encompasses ensuring animals are raised in conditions that respect their well-being and minimizing the environmental impact of animal agriculture. This includes the conditions in which animals are kept, the methods used for shearing or harvesting, and the overall welfare of the animal throughout its life cycle.
Recycled and Repurposed Materials
Sustainable fashion often incorporates recycled or repurposed materials. Recycling textiles reduces the demand for virgin materials, conserving resources and minimizing waste. Repurposing existing materials, such as upcycling old clothing into new items, further minimizes the environmental impact of the fashion industry. By utilizing recycled and repurposed materials, companies can significantly reduce their environmental footprint and contribute to a circular economy.
Certifications and Standards
A plethora of certifications and standards exist to guide and verify ethical practices in the fashion industry. These certifications, such as GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard), Fair Trade, and OEKO-TEX, ensure that certain standards are met regarding environmental and social criteria. Consumers can use these certifications as indicators of ethical sourcing and manufacturing practices. This allows consumers to confidently choose products that align with their values and promote ethical and sustainable fashion choices.
Labor Practices and Fair Wages
Ethical sourcing also encompasses fair labor practices. This means ensuring that workers in the supply chain are treated with respect and dignity, receive fair wages, and work in safe environments. Companies should be transparent about their labor practices, including the wages paid, working hours, and the conditions of employment for their workers. Promoting fair wages and safe working conditions is a cornerstone of ethical sourcing, creating a more equitable and sustainable fashion industry.
Personalized and Sustainable Clothing Solutions
Tailored Experiences for Conscious Consumers
Modern consumers are increasingly seeking personalized experiences, and this trend extends to clothing. Sustainable fashion brands are recognizing this desire and are offering tailored solutions, from curated clothing lines based on individual style preferences to personalized consultations on sustainable choices. This approach not only caters to the customer's need for unique items but also fosters a deeper connection with the brand, encouraging long-term loyalty and reducing fast fashion's environmental impact.
Imagine a future where clothing is not just a purchase but a curated experience. Personalized style guides, tailored to individual needs and preferences, can be a key component of sustainable fashion's future. This personalized approach encourages mindful consumption, reducing the likelihood of impulse buys and promoting the longevity of clothing items.
Eco-Friendly Fabrics and Production Processes
A significant aspect of sustainable clothing is the shift towards eco-friendly materials. This encompasses everything from organic cotton and recycled fabrics to innovative plant-based alternatives. These fabrics are often produced with reduced water and chemical usage, minimizing the environmental footprint of the entire production process. Consumers are increasingly aware of the impact of their clothing choices and are actively seeking out brands that prioritize ethical and sustainable practices throughout their supply chains.
The production processes themselves are also undergoing a transformation. Many brands are adopting more sustainable methods, like reducing water usage in dyeing processes and utilizing renewable energy sources. This commitment to environmentally conscious practices is vital for a truly sustainable fashion industry.
Transparency and Traceability in the Supply Chain
Consumers are demanding greater transparency and traceability in the supply chains of the clothing they purchase. This means knowing the origin of materials, the working conditions in factories, and the environmental impact of the production process. Sustainable brands are responding to this demand by providing detailed information about their supply chains, fostering trust and accountability.
Traceability allows consumers to connect with the story behind their clothes. Knowing where the materials came from and how they were produced empowers consumers to make more informed decisions, supporting businesses that prioritize ethical and environmental responsibility.
Upcycled and Repurposed Apparel
Upcycling and repurposing existing materials are gaining traction as sustainable fashion solutions. Transforming old clothes into new garments, or using discarded materials in new designs, reduces waste and minimizes the need for new resource extraction. This approach not only reduces textile waste but also promotes creativity and innovation in the fashion industry, fostering a circular economy model.
Rent, Resell, and Repair Options
Expanding beyond traditional purchasing models, many sustainable brands are offering rental programs, resale platforms, and repair services. These options allow consumers to access clothing without the commitment of ownership, promoting a more circular fashion system. Repair services extend the lifespan of garments, minimizing waste and reducing the need for constant new purchases.
Rent-to-own, buy-back, and repair services are not just trendy; they are crucial for a sustainable future. These options encourage consumers to think beyond immediate gratification and embrace a more mindful approach to clothing consumption.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Fashion
Technology plays a crucial role in advancing sustainable fashion. From innovative textile production techniques to digital platforms that connect consumers with sustainable brands, technology is transforming the industry. Apps that track the environmental impact of clothing choices, or 3D-printed garments that use less material, are examples of how technology is driving change.
Emerging technologies are helping to create a more sustainable fashion industry. By leveraging innovation, brands can create solutions for reducing waste, minimizing environmental impact, and promoting a more ethical supply chain.