Ethical Fashion for the Future: New Commitments to People
Transparency in Building Materials
Transparency in the building materials industry is crucial for sustainable and ethical practices. Open communication about the sourcing, manufacturing processes, and environmental impact of building materials allows consumers and stakeholders to make informed decisions. This includes disclosing details about the materials' composition, origin, and any potential health or environmental hazards. Providing detailed information empowers consumers to choose products that align with their values and contribute to a healthier planet.
Traceability of Construction Processes
Traceability in construction processes involves meticulously documenting each step of a project, from material sourcing to final installation. This detailed record-keeping ensures accountability and helps identify potential issues early on. By linking specific materials and components to their origins, manufacturers and builders can track potential defects or substandard practices. This enhanced visibility also supports quality control and enables quicker responses to any problems that may arise, ultimately leading to greater reliability and safety in construction projects.
Supply Chain Transparency
A transparent supply chain is essential for responsible building material procurement. This means fully disclosing the origin of materials, the labor practices used in manufacturing, and the environmental impact of the entire process. Providing this level of detail helps consumers make ethical choices, and promotes fair wages and safe working conditions in supply chain operations. Ultimately, transparency in the supply chain helps build trust and fosters a more sustainable construction industry.
Impact on Sustainability
Transparency and traceability in building materials and construction processes have a profound impact on sustainability initiatives. By providing clear information about the environmental footprint of products, builders and consumers can make conscious choices that minimize their ecological impact. This includes considering factors like the embodied carbon in materials and the energy efficiency of building designs.
Ethical Considerations
Transparency and traceability are key elements in ensuring ethical practices in the construction industry. By disclosing the sourcing and manufacturing processes, companies can demonstrate their commitment to fair labor practices and environmental responsibility. This commitment fosters trust among stakeholders and promotes a more just and equitable industry. Transparency also helps to identify and address potential human rights violations in the supply chain.
Improved Collaboration and Communication
Implementing transparency and traceability fosters better collaboration among all stakeholders involved in a construction project. Clear communication about materials, processes, and potential risks facilitates a smoother workflow and reduces the likelihood of disputes or errors. Improved communication builds stronger relationships between clients, contractors, and suppliers, leading to more efficient and successful projects. This collaborative approach is fundamental to the long-term success of any building project.
Fair Labor Practices: Ensuring Dignity and Respect for Workers
Understanding Fair Labor Practices
Fair labor practices are crucial in the ethical fashion industry, encompassing a wide range of principles that prioritize the well-being and dignity of workers throughout the supply chain. These practices extend beyond simply adhering to minimum wage laws and encompass a commitment to safe working conditions, reasonable hours, freedom from coercion, and opportunities for advancement. Ethical fashion businesses must actively seek to understand and address the needs of their workers, recognizing their inherent value and promoting a respectful environment.
Wage and Compensation Equity
Ensuring fair wages and compensation is fundamental to fair labor practices. This means paying workers a living wage that allows them to meet their basic needs and participate fully in society. It also includes providing benefits like health insurance, paid time off, and retirement plans, reflecting a commitment to the long-term well-being of employees. Transparency in compensation structures is essential to build trust and demonstrate a commitment to equitable treatment.
Companies should actively research and understand the local cost of living and prevailing wage rates in the regions where they operate. This ensures that workers are not exploited by being paid significantly below the market rate.
Safe Working Conditions and Health
Worker safety and health are paramount in fair labor practices. This includes creating workplaces free from hazards, providing appropriate safety equipment, and ensuring access to necessary medical care. Ethical fashion companies must implement robust safety protocols and conduct regular safety inspections to protect workers from accidents and illnesses. Prioritizing worker health extends to providing resources and education on occupational hazards, promoting preventative measures, and allowing for sick leave.
Freedom from Coercion and Harassment
Workers should be free from any form of coercion, intimidation, or harassment. This includes ensuring freedom of association, the right to organize, and the ability to voice concerns without fear of reprisal. Ethical fashion businesses should actively foster a culture of respect and open communication, where employees feel empowered to report any instances of abuse or unfair treatment without fear of retribution.
Hours and Overtime Policies
Fair labor practices dictate reasonable working hours. Companies must adhere to legal limits on working hours, provide adequate rest periods, and refrain from excessive overtime without proper compensation. Implementing clear policies regarding overtime and ensuring adherence to these policies is crucial to preventing worker burnout and ensuring their well-being.
Opportunities for Advancement and Training
Providing opportunities for skill development and career growth is a key aspect of fair labor practices. Investing in training programs, offering apprenticeships, and promoting from within are essential to empowering workers and fostering a sense of loyalty and belonging within the company. These initiatives show a commitment to the long-term growth and development of employees beyond their immediate roles.
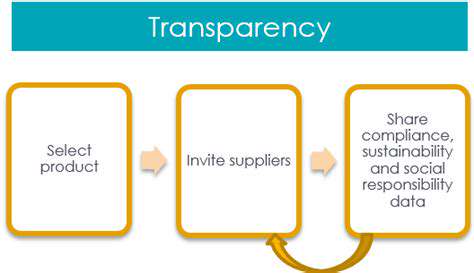
Transparency and Accountability
Transparency and accountability are essential components of fair labor practices. Companies should be open about their supply chain, their labor practices, and their commitment to ethical standards. This includes providing access to information about wages, working conditions, and any potential issues that arise. Independent audits and certifications can further enhance transparency and accountability, assuring consumers of a company's commitment to ethical practices.
Biodegradable plastics are a class of plastics that break down into natural elements like water, carbon dioxide, and biomass under specific environmental conditions. These materials are often derived from renewable resources such as corn starch, sugarcane, or algae, offering a potential solution to the persistent problem of plastic waste. However, the effectiveness of biodegradability is heavily reliant on the specific conditions, and it's not a guaranteed solution for all plastic-related issues. Proper composting facilities are often required for complete breakdown, and some bioplastics can still leach harmful chemicals into the environment if not processed correctly.
Sustainable Materials and Production Methods: Minimizing Environmental Impact
Exploring Sustainable Materials
Sustainable materials are crucial in minimizing environmental impact. The selection of raw materials significantly influences the environmental footprint of a product throughout its lifecycle. Using recycled materials, renewable resources, and bio-based alternatives can drastically reduce the reliance on finite resources and the associated emissions from extraction and processing. This shift towards sustainability requires a comprehensive understanding of material properties, availability, and the environmental impacts of their entire lifecycle.
Innovative research and development are essential for discovering and refining sustainable alternatives to traditional materials. This includes exploring new polymers derived from plant-based sources, developing advanced composites with lower environmental burdens, and finding ways to improve the recyclability and reusability of existing materials.
Optimizing Production Processes for Sustainability
Manufacturing processes are a major contributor to environmental pollution, from greenhouse gas emissions to water contamination. Implementing sustainable production methods involves minimizing energy consumption, reducing waste generation, and adopting cleaner technologies. This includes optimizing energy efficiency throughout the production process, utilizing renewable energy sources, and implementing closed-loop systems for material recovery and reuse.
By focusing on resource efficiency, manufacturers can significantly reduce their environmental footprint. This involves minimizing material waste, using water more efficiently, and employing processes that generate less pollution. The adoption of lean manufacturing principles and waste reduction strategies can further enhance sustainability efforts.
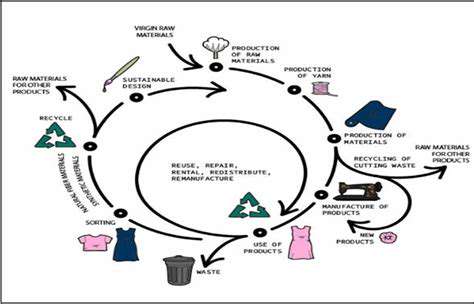
The Role of Circular Economy Principles
Adopting circular economy principles is vital for minimizing environmental impact across the product lifecycle. This approach focuses on designing products for disassembly, reuse, and recycling. By incorporating elements of design for durability, repairability, and recyclability, manufacturers can create products that can be easily disassembled and their materials recovered for reuse in new products, thereby minimizing waste and resource depletion.
The circular economy model promotes a shift from a linear take-make-dispose approach to a cyclical system. This paradigm shift requires a holistic view of the product lifecycle, involving all stakeholders from design to end-of-life management, enabling a more sustainable approach to material and resource management.
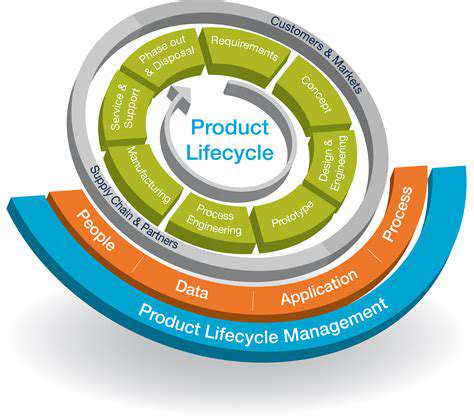
Life Cycle Assessment and Environmental Impact Analysis
Thorough life cycle assessments (LCAs) are essential tools for evaluating the environmental impact of materials and products. LCAs provide a comprehensive analysis of the environmental effects associated with each stage of a product's lifecycle, from raw material extraction to disposal. This systematic approach helps to identify areas where improvements can be made to minimize the environmental footprint.
Environmental impact analyses, combined with LCA findings, enable informed decision-making regarding material selection and production methods. This data-driven approach ensures that sustainable choices align with minimizing environmental impacts and maximizing resource efficiency.
Promoting Responsible Consumption and Waste Management
Encouraging responsible consumption patterns and effective waste management strategies are crucial elements of a sustainable approach. Consumers play a vital role in reducing their environmental impact by opting for products made from sustainable materials, minimizing their consumption, and properly disposing of waste. Education and awareness campaigns can empower consumers to make informed choices that align with environmental sustainability.
Collaboration and Policy Support for Sustainability
Collaboration among businesses, governments, and consumers is essential for driving the adoption of sustainable materials and production methods. Public-private partnerships can foster innovation and facilitate the transition towards a more sustainable future. Governments can play a significant role in promoting sustainability through supportive policies and regulations. This includes incentives for the development and adoption of sustainable technologies and materials.
Developing and implementing robust policies and regulations that incentivize sustainable practices can significantly accelerate the shift towards environmentally conscious materials and production methods. These policies should encourage the use of renewable resources, promote the adoption of circular economy principles, and mandate environmental impact assessments for products and processes.